1. Automatic driving classification
Different organizations have different grading standards for autonomous driving: the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) divides autonomous driving into five levels, while the International Society of Automated Mechanical Engineers (SAE) standards are divided into six groups of L0~L5. Level, the classification of L0, L1, L2 is the same, the difference is that the L4 of NHTSA is subdivided into L4 and L5 by SAE. There are many SAE standards adopted in China.
L0: Full human driving.
L1: Auxiliary driving, adding ADAS functions such as lane departure warning (LDW), forward collision warning (FCW), blind spot detection (BSD), etc.
L2: Partial autopilot with ADAS functions for intervention assistance, including adaptive cruise (ACC), emergency automatic brake (AEB), and lane keeping assist (LKA).
L3: Conditional automatic driving, with comprehensive intervention assistance functions, including automatic acceleration, automatic braking, automatic steering, etc.
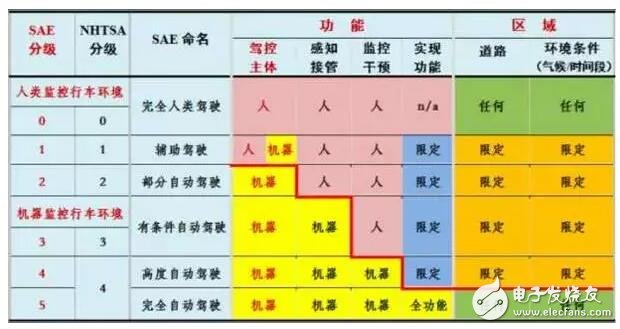
The essential changes have taken place from L2 to L3. L2 and below are still used to observe the driving environment. It is necessary to have a driver in the driver's seat and take over directly in case of emergency. The L3 class and above are used by the machine to observe the driving environment. The human driver does not need to sit in the driver's seat and hold the steering wheel. It is only necessary to have a monitoring computer in or outside the vehicle. In an emergency, the cognitive operation is performed by computer operation.
L4: Highly self-driving, without any human driver, without steering wheel, throttle, brake pedal, but limited area (such as park, scenic area), or limited environmental conditions (such as rain and snow, night can not open).
L5: Fully automatic driving, it is a real driverless stage, no driver position, no cognitive intervention in the car or outside the car; no steering wheel and throttle, brake pedal; full area, full function.
Nowadays, there are many companies that can achieve unmanned driving in a specific park, claiming that they have reached the L4 level. Is the level of driverless technology at this stage really so high? This is a bit confusing. In the closed environment, the unmanned driving of the L4 level in the fixed route and the automatic driving of the L2 level in the urban area of ​​Beijing are more technically difficult? It must be self-evident. Therefore, L4 must be more advanced than L2 and L3. It is necessary to look specifically at the area of ​​automatic driving (closed, open; area size, complexity), function, and environmental conditions (climate, time period).
2. The path of automatic driving
Auto-driving winds are coming, and technology companies, start-ups, emerging electric car companies, traditional car companies, and Tier 1 suppliers are rushing into each other. At present, there are two typical technical paths: one is a one-step type represented by cross-border technology companies and start-ups. It crosses the middle level and refers to L4 and L5 unmanned driving. After maturity, the cost will drop and then be commercialized on a large scale. There is also a gradual and progressive type represented by traditional car companies and TIer1. They promote the commercialization of the assisted driving function at an acceptable cost, and then gradually transition to unmanned driving as the ADAS function is improved and upgraded.
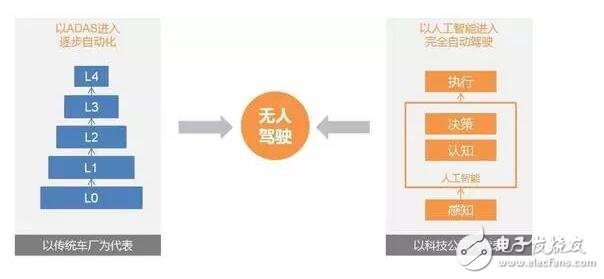
The problem with the first path is that the technology companies do not have the capacity to produce cars. The amount of data collected by the test vehicles is naturally not as much as the number of ADAS systems installed in each vehicle. The problem with the second path is the splicing of various ADAS functions. Can it form a complete driverless system?
The strengths of technology companies are in the advantage of artificial intelligence technology, but they lack experience in automotive engineering. The threshold for building a car is very high. The traditional car enterprise has the advantage of the whole industry chain, the product safety and reliability are higher, and consumers have higher recognition of its brand, and the automobile industry will not be completely subverted by the technology company. Traditional car companies have rich experience in the whole vehicle and a perfect aftermarket. However, with the advent of electric vehicles and automatic driving, the traditional car companies have a strong sense of crisis, and they are afraid to become a foundry. The research and development of autonomous driving is basically based on the new energy vehicle platform, bypassing the barriers such as the engine and the gearbox. The motor, battery and electronic control core system of the electric vehicle have shaken the competitive advantage of the traditional car enterprise in the “powertrainâ€. The two camps have their own advantages and disadvantages and are irreplaceable. At present, they are increasingly moving towards open marriage in the form of cooperation and investment.
IDC Series Centronic Connector
IDC Series Centronic Connector
Current Rating:5A
Dielectric Withstanding Voltage:1000V for one minute
Insulation Resistance:1000MΩ Min.(at 500V DC)
Contact Resistance:35mΩ Max.
Temperature:-55°C to +105°C
IDC Series Centronic Connector
ShenZhen Antenk Electronics Co,Ltd , https://www.atkconnectors.com