IPsec (IP Security) is a three-layer tunnel encryption protocol developed by the IETF that provides high-quality, interoperable, cryptographic-based security for data transmitted over the Internet. The following communication services are provided by specific communication parties at the IP layer through encryption and data source authentication:
ConfidenTIality: The IPsec sender encrypts the packet before transmitting it over the network.
Data Integrity: The IPsec receiver authenticates the packet sent by the sender to ensure that the data has not been tampered with during transmission.
Data AuthenTIcaTIon: IPsec can authenticate the sender of the IPsec packet at the receiving end.
Anti-Replay: IPsec receivers can detect and reject incoming or outdated messages.
IPsec has the following advantages:
Supports IKE (Internet Key Exchange), which implements auto-negotiation of keys and reduces the cost of key negotiation. The SA service can be established and maintained through IKE, which simplifies the use and management of IPsec.
All applications and services that use the IP protocol for data transmission can use IPsec without having to make any modifications to these applications and services themselves.
Encryption of data is based on packets, not on the entire data stream. This is not only flexible but also helps to further improve the security of IP packets, which can effectively prevent network attacks.
IPSec goals
l Provide strong interoperability for IPv6 and IPv6
l High quality password-based security
l Implement multiple security services at the IP layer, including: access control, connectionless integrity, data source authentication, anti-replay, confidentiality, and limited traffic flow confidentiality.
IPSec security architecture diagram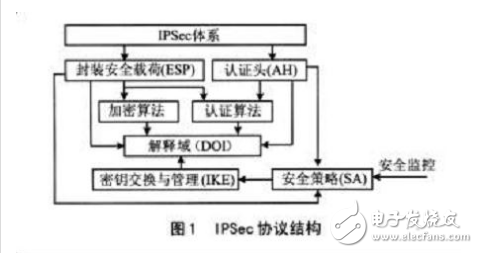
IPSec security system content
Verify header AH:
Provide data integrity check and identity authentication functions for IP packets;
The verification algorithm is specified by the SA;
The scope of certification: the entire package.
Package security payload ESP:
Provide security services such as confidentiality, data source verification, anti-replay and data integrity;
Briefly describe how ipsec worksBoth the encryption algorithm and the authentication method are specified by SA.
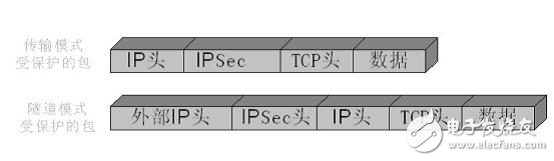
Used in two modes: transfer mode and tunnel mode
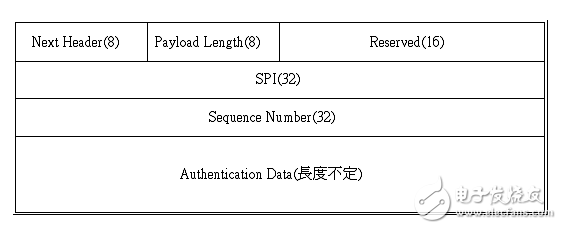
AH header format
AH transmission mode
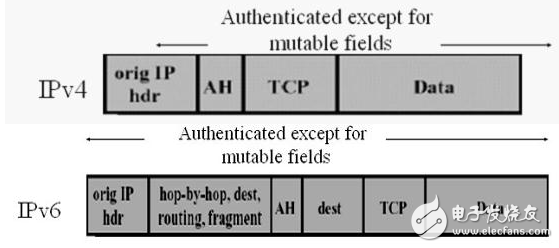
AH tunnel mode
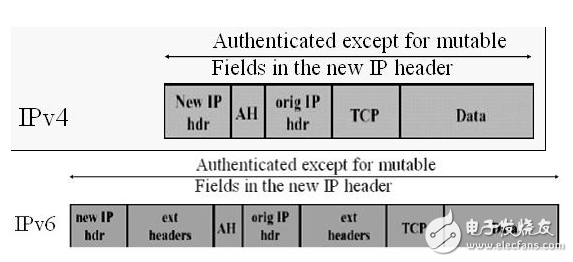
AH processing
1) Processing AH for the processing of outgoing packets
l Create an outbound SA (manually or through IKE)
l Produce a good sequence
l Fill the fields of the AH header
l Calculate ICV (Integrity Check Value)
The content includes: part of the domain in the IP header, AH itself, upper layer protocol data
l The "next header" in the AH header is set to the value of the "protocol" field in the original IP header. The protocol field of the original IP header is set to 51 (representing AH).
2) For the received package processing:
l Slice assembly
l Find SA
Basis: Target IP address, AH protocol, SPI
l Check the serial number
l ICV inspection
ESP header format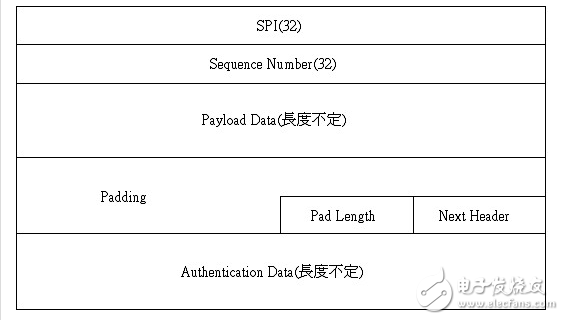
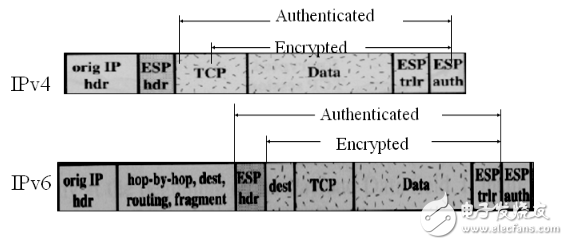
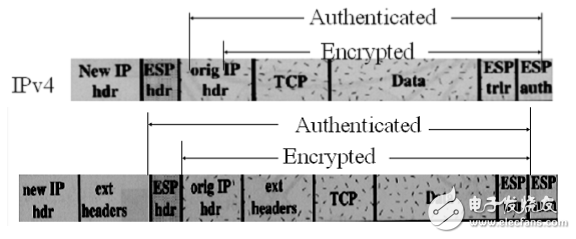
1) Handling of the package that is going out
l Find SA
l encryption
l Encapsulate the necessary data and put it in the payload data field. Different modes, the range of encapsulated data is different.
l Increase the necessary padding data
l Encryption operation
l verification
l Calculate ICV Note: Calculate the encrypted data
2) Processing of the received package
l Slice assembly
l Find SA
Basis: target IP address, ESP protocol, SPI
l Check the serial number (optional, for replay attacks)
Use a sliding serial port to check the playback of the serial number
l ICV inspection
l decrypt
Decrypt the data of the encrypted part according to the algorithm specified in the SA and the missing, parameter
Remove padding
Refactoring the original IP packet
SA (Security Association) Security Alliance
l SA is one-way (can not be reversed)
l SA is "protocol-related" (corresponding to the agreement)
l Each SA is marked with three parameters, "spi, dst(src), protocol"
Security Parameter Index (SPI)
IP address of the other party
Security protocol identifier: AH or ESP
l SA is related to two databases implemented in the IPSec system.
Security Policy Database (SPD)
Security Association Database (SAD)
Key Management
l ISAKMP defines a key management framework. ISAKMP is the same as IKE, and IKE is an advanced version.
l IKE is a bus. It is really a key exchange protocol for IPSec.
ISAKMP refers to the RFC2308 document, and the IKE protocol refers to the RFC2409 document.
Two-stage exchangePhase 1: Establishing ISAKMP SA - IKE SA
Both parties (such as ISAKMP Sservers) agree on how to protect future communications, and the two parties establish a channel through identity authentication and security protection;
This SA will be used to protect the negotiation process of the protocol SA of the latter table.
Phase 2: Establishing SA for other security protocols - IPSec SA
This stage can establish multiple SAs;
This SA will be used by the corresponding security protocol for the exchange of Boahu data or messages.
IPSec-VPN protocol and algorithmIP security protocol: AH, ESP
Data Encryption Standard: DES, 3DES
Public Key Cryptography Protocol: Diffe-Hellman (DH)
Hash algorithm: MD5, SHA-1
Public key encryption algorithm: RSA
Internet Key Exchange: IKE
Certificate Authority: CA
New Smart Watch
New Smart Watch
everyone enjoys luck , https://www.eeluck.com