The structure of the current transformer is relatively simple, and consists of a primary winding, a secondary winding, a core, and a frame, a casing, a terminal, and the like insulated from each other. The working principle is basically the same as that of the transformer. The number of turns (N1) of the primary winding is less, directly connected in series with the power line. When the primary load current (I1) passes through the primary winding, the alternating magnetic flux induced is proportionally reduced. Secondary current (I2); the number of turns (N2) of the secondary winding is large, and the closed circuit is formed in series with the secondary load (Z) of the current coil of the instrument, relay, transmitter, etc., as shown in Fig. 1.
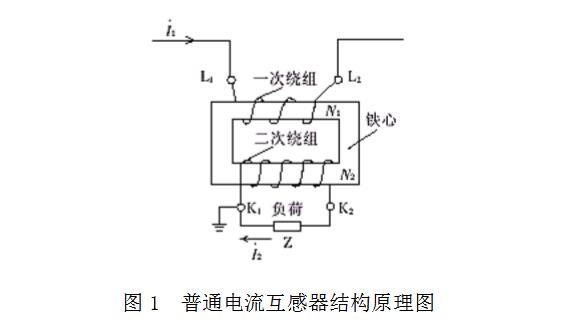
Since the primary winding has the same ampere-turns as the secondary winding, I1N1=I2N2, the current transformer rated current ratio: 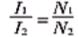 . In the actual operation of the current transformer, the load impedance is small, and the secondary winding is close to the short-circuit state, which is equivalent to a short-circuiting transformer.
. In the actual operation of the current transformer, the load impedance is small, and the secondary winding is close to the short-circuit state, which is equivalent to a short-circuiting transformer.
The feedthrough type current transformer has no primary winding in its own structure, and the current carrying (load current) wire acts as a primary winding from L1 to L2 through a circular (or other shape) core made of silicon steel sheet coil. The secondary winding is directly and evenly wound on the circular core, and forms a closed loop in series with the secondary load of the current coil of the meter, relay, transmitter, etc., as shown in Fig. 2.
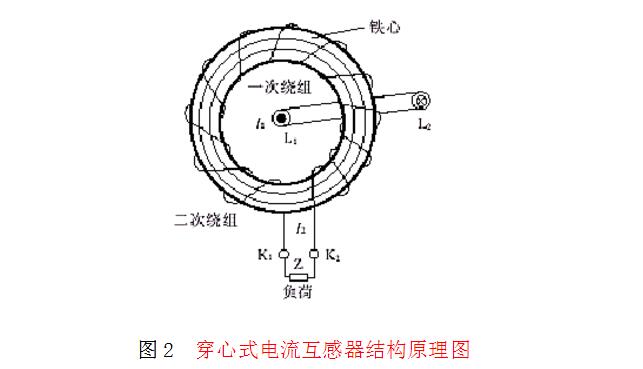
Since the through-type current transformer does not have a primary winding, the ratio is determined according to the number of turns of the primary winding passing through the core of the transformer, and the more the number of penetrating turns, the smaller the ratio; on the contrary, the fewer the number of penetrating passes, The larger the ratio, the rated current ratio: 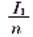
In the formula I1 - a rated current when passing through the heart;
n - through the heart.
3. Structure principle of special type current transformer1) Multi-tap current transformer
The multi-tap current transformer has the same primary winding. When winding the secondary winding, several taps are added to obtain a plurality of different ratios. The utility model has an iron core and a primary winding with a fixed number of turns, and the secondary winding is wound on the insulating cylinder set on the iron core with an insulated copper wire, and the taps of different ratios are taken out and connected to the terminal block, each The taps are provided with respective terminals, thus forming a plurality of ratios.
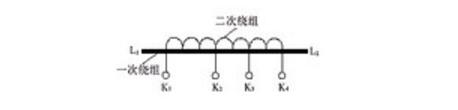
Graphic: Schematic diagram of the structure principle of multi-tap current transformer
2) Multi-variable current transformer
Although the multi-ratio current transformer and the multi-tap current transformer are different in different ratios by adding multiple sets of secondary windings, the secondary winding of the multi-ratio current transformer is divided into two (or more) turns. The different number of independent windings meet the needs of different ratios and different accuracy levels under the same current condition.
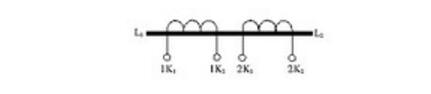
Illustration: Schematic diagram of multi-ratio current transformer structure
3) Winding adjustable current transformer
The winding adjustable current transformer is a current transformer with adjustable primary winding and secondary multiple windings. The current transformer is characterized by a variable ratio range and can be arbitrarily changed, and is mostly applied to a high voltage current transformer.
The primary winding of the winding adjustable current transformer is divided into two sections, which respectively pass through the iron core of the transformer, and the secondary winding is divided into two independent windings with taps and different accuracy levels. The primary winding is connected to the connecting piece on the outside of the transformer. By changing the position of the connecting piece, the primary winding is formed in series or parallel connection (as shown in the following figure, the schematic diagram of the series connection and the parallel structure), so by changing the number of turns of the primary winding , you can get different ratios. The tapped secondary winding itself is divided into two (or more) windings with different ratios and different accuracy levels. As the position of the primary winding tab changes, the number of turns of the primary winding changes accordingly, and the ratio is also changed. Change, so that a multi-range ratio is formed.
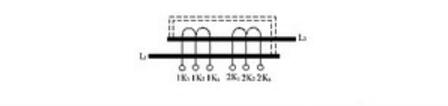
Illustration: Schematic diagram of winding adjustable current transformer structure (one-time serial connection) 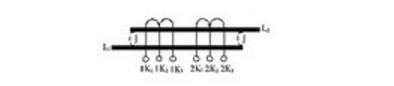
Illustration: Schematic diagram of winding adjustable current transformer structure (one parallel connection)
How does the current transformer look at the magnification?The current ratio of the transformer is generally marked by the primary (through the core) 1åŒ. According to the current ratio equal to the turns ratio, the current ratio when the core is 1åŒ is equal to: 150/5/1 is equal to 30 times, and the current is 2 times. Ratio is equal to 150/5/2 equals 15 times,
150/5 current transformer 1 åŒ through the heart, 30 times. 2 åŒ wear heart, 15 times. 3 åŒ wear heart, 10 times 5 åŒ through the heart, 6 times. In short, you use the rate of wearing a heart, divided by the number of heart, is the actual rate.
The magnification mainly depends on the magnitude of the primary current and the current measured or controlled by the secondary side. Generally, the secondary side nominal current of the current transformer is 5A. The main reason is to select the appropriate current transformer primary current nominal value (close to the transformer nominal current value) according to the supply current of the AC power source or the current of the power load.
For example, if the rated current of the power distribution cabinet to a certain line is 1450A, then the current transformer of 1500A/5A should be selected, and the three-phase 5A watt-hour meter should be used, then the magnification is 150.
Current transformer primary core turns and magnification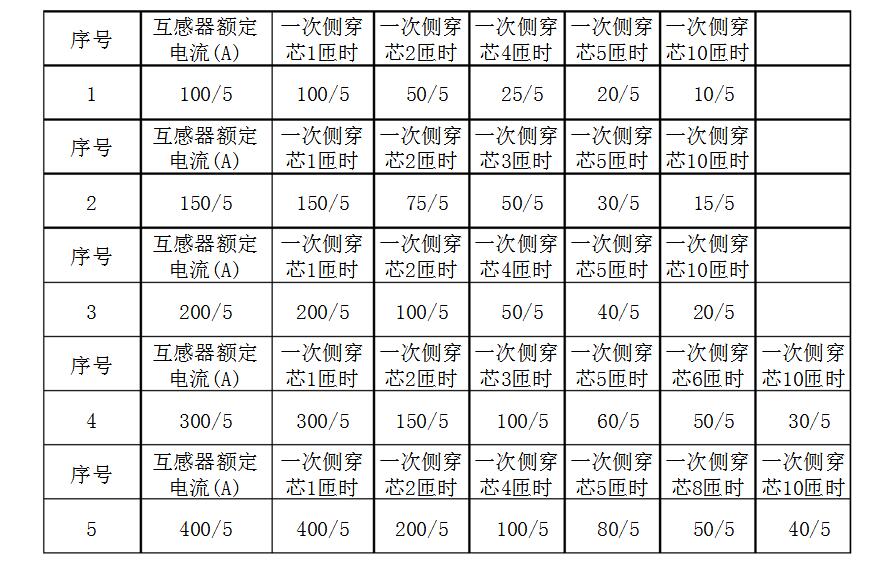
Easy Electronic Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.yxpcelectronicgroups.com