This article is mainly about the relevant introduction of Samsung 788DF, and focuses on the detailed description of the scanning circuit and circuit principle of Samsung 788DF.
Analysis of internal structure circuit diagram of Samsung 788DF displayThe Samsung 788DF color monitor is compatible with VGA, SVGA, VESA, supports VESA flicker-free mode, the picture is stable and perfect, meets the "plug and play" function, provides intelligent power saving function, OSD screen adjustment function display, intuitive and convenient operation, and easy to use. The field scan chip STV9118 has a concise circuit structure. As shown in the figure, it is the circuit composition of Samsung 788DF.
It can be seen from the circuit diagram of the whole machine that the Samsung 788DF color display mainly uses line and field small signal processing integrated circuit IC401 (STV9118), line output, field output integrated circuit IC301 (STV9325), microprocessor IC201 (KS88C6232N), memory IC241 (KS24C081), video signal processing circuit IC102 (NT6813), video output circuit IC106 (STV9588) and switching power supply control circuit IC601 8S0765RRC (FS8S0765RRC) are the core components.
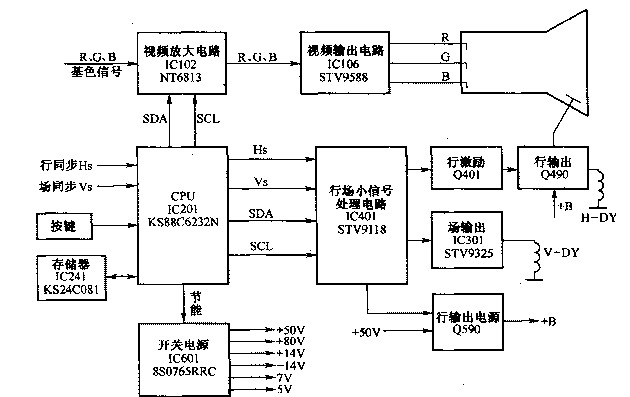
The Samsung 788DF color monitor is compatible with VGA, SVGA, VESA, supports VESA flicker-free mode, the picture is stable and perfect, meets the "plug and play" function, provides intelligent power saving function, OSD screen adjustment function display, intuitive and convenient operation, and easy to use. The field scan chip STV9118 has a concise circuit structure. As shown in the figure, it is the circuit composition of Samsung 788DF.
It can be seen from the circuit diagram of the whole machine that the Samsung 788DF color display mainly uses line and field small signal processing integrated circuit IC401 (STV9118), line output, field output integrated circuit IC301 (STV9325), microprocessor IC201 (KS88C6232N), memory IC241 (KS24C081), video signal processing circuit IC102 (NT6813), video output circuit IC106 (STV9588) and switching power supply control circuit IC601 8S0765RRC (FS8S0765RRC) are the core components.
Samsung 788DF field scanning circuit diagram detailedThe scanning circuit of the machine is composed of RGB three primary color signal preamplifier circuit IC102 (NT6813), RGB three primary color signal output amplifier circuit IC106 (STV9588), and the auxiliary circuit of the picture tube as the core structure.
1. Pre-amplification circuit
The pre-amplification circuit is composed of IC102 (NT6813) as the core, and the pin functions of NT6813 are shown in Table 11-4.
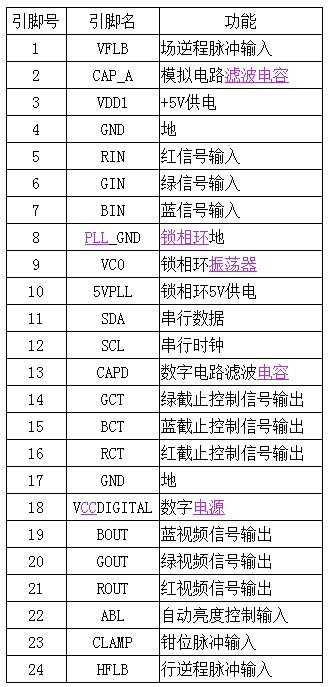
The R, G, and B three-way analog signals output by the computer host are input to the video signal processing circuit board through the connector. Among them, the R primary color signal is sent to the 5 pin of the NT6813 through RR02 and CR01, and the G signal is sent to the NT6813 through the RG02 and CG01. At pin 6, the B signal is sent to pin 7 of NT6813 via RB02 and CB01. After being amplified by NT6813, the R, G, and B signals are output from 21, 20, and 19 pins.
The 23 pin of NT6813 is the clamp pulse input terminal. Under the action of the clamp pulse, the video clamp circuit is in working state, so that the 21 pin, 20 pin, and 19 pin of NT6813 have video signal output. If the NT6813 has no clamp pulse voltage input, the R, G, and B amplifiers of the NT6813 will be cut off, and the picture tube will be black.
2. Video output circuit
The video output circuit is composed of IC106 (STV9588) as the core. STV9588 pin functions are shown in Table 11-5.
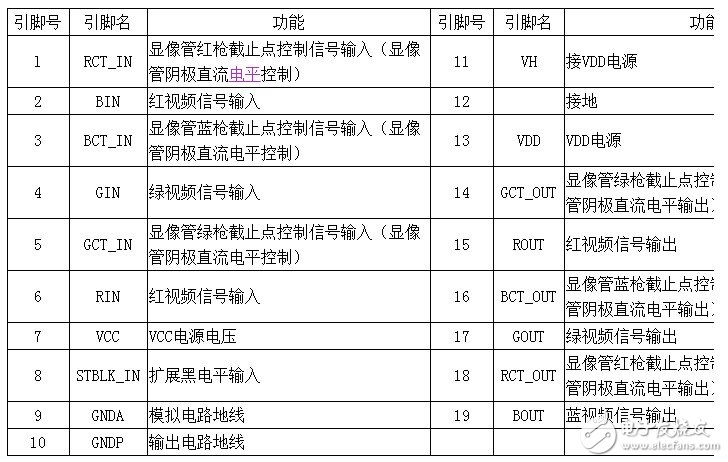
The R, G, and B signals output from the 21, 20, and 19 pins of the NT6813 are added to the 6, 4, and 2 pins of the STV9588 respectively. After being amplified by the STV9588, the R, G, and B primary color signals are output from the 15, 17, and 19 pins respectively. It is coupled to the three cathodes of RK, GK and BK of the picture tube via CR04, CG04 and CB04.
LR01, LG01, LB01 are used to improve the high-frequency quality of the picture. DR05, DR03, DG05, DG03, DB05, DG03 are set to prevent the STV9588 from sparking and damaging the picture tube. SKR01, SKG01, and SKB01 are electric dischargers, and their function is to prevent the damage caused by the ignition of the picture tube.
3. White balance adjustment circuit
1. Dark balance adjustment The dark balance adjustment is to adjust the static working voltage of the picture tube RK, GK, BK, so that the cut-off points of the three electron beams are moved to the same position to ensure that the screen does not cast color at low brightness.
When the cathode potential of the kinescope RK needs to be changed, the microprocessor IC201 changes the DC voltage output by the 16-pin of the NT6813 through the I2C bus. After processing by IC106 (STV9588), it controls the 18-pin DC potential of the STV9588 to change, thereby controlling the CRT's RK cathode potential. The adjustment process of the cathode potential of GK and BK is no longer analyzed.
2. Bright balance adjustment Bright balance is achieved by changing the gain (signal amplitude) of the R, G, and B primary color signals to ensure that the picture does not cast color at high brightness.
When the R signal gain needs to be changed, the microprocessor IC201 controls the NT6813's R channel amplifier signal gain to change through the II2C bus, and then controls the NT6813's 21 pin output to change the R signal amplitude. The adjustment process of G and B signal gain is no longer analyzed.
Four, contrast and ABL control circuit
1. Contrast control circuit Contrast is achieved by controlling the gain of the three primary color signals of R, G, and B. When it is necessary to increase the contrast, the microprocessor IC201 controls the gain of the R, G, B three-channel amplifiers of the NT6813 through the I2C bus to increase, so that the picture contrast can be increased.
When reducing the contrast, the control process is reversed.
2. ABL control circuit. When the brightness of the picture increases and the current of the picture tube bundle increases, the voltage of pin 8 of the line output transformer T501 drops, which causes the voltage of pin 22 of NT6813 to drop, and controls the gain of the internal R, G, B amplifiers to decrease, so that the picture tube The beam current is reduced to avoid the harm caused by excessive beam current.
Five, brightness control and elimination of bright spots circuit
1. Brightness control circuit
The brightness control circuit of this machine does not adopt the common grid control method, but adopts the cathode control method.
The video amplifier output adopts AC output mode. The video amplifier output is a clamped video signal. Therefore, the brightness of the grating depends on the DC level (black level) of the cathode of the kinescope. The brightness control circuit is controlled by the microprocessor IC201 through the IIC bus. The signal processing circuit NT6813 is completed. When the brightness needs to be adjusted, the DC voltage output by the 21, 20, and 19 pins of the NT6813 will change at the same time. After the STV9588 is processed, the DC voltage output by the 18, 14 and 16 pins of the STV9588 will be changed at the same time, and then the DC voltage of the cathode of the kinescope will be controlled. The brightness of the grating changes to achieve the purpose of brightness control.
2. Eliminate the bright spot circuit
The negative pulse voltage on the 9th pin of the secondary winding of the line output transformer T501 is rectified and filtered by D504 and C505 to obtain a negative voltage of -150V. When the display is working, the transistor Q512 is always on because the emitter voltage is always higher than the base voltage, so the -150V voltage is divided by R514, R515, Q512 and then applied to the grid G1 of the picture tube, which is The picture tube grid provides the negative pressure required for normal operation. After the display is turned off, Q512 cuts off quickly, and the -150V voltage is directly applied to the picture tube grid G1 without being divided by Q512. Because of this large negative pressure, the electron beam can be cut off and the shutdown bright spot is eliminated.
Six, line and field blanking circuit
1. Line blanking circuit
The line blanking is not applied to the grid of the kinescope, but the line retrace pulse from the line scan output circuit is applied to the video signal processing circuit NT6813 to complete the line blanking. The specific working process is: the line retrace pulse generated by the line scan circuit is added to the 24 feet of the NT6813. The scan can be blanked during the reverse travel period to avoid retrace lines appearing on the phosphor screen.
2. Field blanking circuit
Field output integrated circuit IC301 (STV9325) of the 3-pin output field flyback pulse V-BLK, C307, R311 added to the base of Q512, Q512 inverted and output from the collector, during the vertical blanking period, it is added to The voltage drop (more negative) of the G1 pole of the picture tube reduces the brightness of the screen scene and achieves the purpose of eliminating the field retrace line.
Seven, video squelch circuit
At the moment of power-on or mode change, the 8-pin of the microprocessor IC201 outputs a short high level, controls Q511 to turn on, and Q512 to turn off, so that the negative pressure on the G1 pole reaches the negative maximum value, and the grating on the phosphor screen disappears. Video squelch.
Display circuit diagram analysisDisplay circuit diagrams mainly include block diagrams, unit circuit diagrams, integrated circuit internal block diagrams, complete machine circuit diagrams, printed board diagrams, etc., but for maintenance staff, it is usually enough to understand circuit diagram block diagrams, circuit schematic diagrams and printed board diagrams.
1. Block diagram
(1) Introduction to the block diagram
A block diagram is a circuit diagram that uses various blocks and connections to show the working principle and composition of the circuit. The difference between it and the schematic diagram is that the schematic diagram specifically draws all the components of the circuit and their connection methods, while the block diagram simply divides the circuit into several parts according to functions, and depicts each part as a box. Mark simple text descriptions in the boxes, and use lines between the boxes to illustrate the relationship between the boxes.
Of course, the block diagram is simple, but it is very important for both beginners and experienced technicians. As long as you really grasp the block diagram of the liquid crystal display and understand the role of each functional block in the circuit, it will make the maintenance work more handy.
2. Types of block diagrams
There are many types of block diagrams, and the details are as follows:
(1) Block diagram of the complete circuit
The circuit block diagram of the whole machine is a block diagram that expresses the circuit diagram of the whole machine. From this block diagram, you can understand the circuit composition of the whole machine and the relationship between each part of the unit circuit. Through the arrows in the figure, you can also understand the signal transmission path.
(2) System circuit block diagram
A complete machine circuit is composed of many system circuits, and the system circuit block diagram is used to show the composition of the system circuit. It is the next level block diagram of the complete circuit block diagram, which is often more specific than the complete circuit block diagram.
(3) Block diagram of the internal circuit of the integrated circuit
The internal circuit composition of an integrated circuit can be represented by internal circuits or internal circuit block diagrams. Because the internal circuit of the integrated circuit is very complicated, it is more beneficial to read the picture by using a block diagram in many cases. From the internal circuit block diagram of the integrated circuit, you can understand the composition of the integrated circuit, the role of the relevant pins, etc., which is very useful for reading the application circuit of the integrated circuit. Generally, an integrated circuit has more pins and more complicated internal circuit functions, so it is most convenient to give a block diagram of the internal circuit of an integrated circuit during circuit analysis.
3. The function of the block diagram
The block diagram has the following functions:
(1) Roughly express the composition of a circuit (which can be a complete circuit, a system circuit, a functional circuit, etc.), usually the location and name of the main unit circuit of this circuit, and the connection between each part of the unit circuit relationship.
(2) The signal transmission direction between each unit circuit is expressed, so that the transmission order of the signal between each part of the unit circuit can be understood intuitively.
(3) According to the circuit name marked in the block diagram, we can know the processing process of the signal in this unit circuit, which can provide guiding information for analyzing the specific circuit.
The block diagram is an important circuit diagram, especially when reading integrated circuit application circuit diagrams, complex system circuits, and understanding the overall circuit composition, if there is no block diagram, it will cause many inconveniences and difficulties in reading the diagram.
4. Recognition method of block diagram
When understanding the signal transmission process in the circuit diagram of the whole machine, it is mainly to look at the direction of the arrow in the figure. The loop where the arrow is located indicates the transmission path of the signal, and the direction of the arrow indicates the transmission direction of the signal.
When analyzing the composition of a circuit system, the block diagram can be used to see the relationship between the various parts of the circuit, that is, how the parts are connected. Especially the microcontroller circuit of the liquid crystal display, you can see the transmission process of the control signal, the origin of the control signal and the object of control.
When reading the application circuit of an integrated circuit, when there is no pin function information of the integrated circuit, you can use the internal circuit block diagram of the integrated circuit to determine the pin function, especially to understand which pins are input pins and which are output pins. . The arrow of the pin lead pointing to the outside of the integrated circuit is the output pin, and the arrow pointing inward is the input pin. In addition, in some integrated circuit block diagrams, the arrows on some pins are bidirectional, indicating that the signal can be input and output.
5. Circuit schematic
The circuit schematic diagram directly reflects the structure and working principle of the electronic circuit. In the maintenance work, by identifying the various circuit component symbols in the diagram and the connection between them, you can understand the actual working conditions of the liquid crystal display circuit.
The circuit schematic diagram can completely express the structure and working principle of a certain level of circuit or the whole machine, and sometimes the parameters of the circuit components, such as resistance, capacity, and transistor model, are also marked in the diagram.
The circuit schematic diagram adopts the customary drawing method, which makes people understand at a glance. For example, the components adopt the customary drawing method, and the shortest connection lines are used between the components. In the actual circuit of the whole machine, due to the constraints of the components in other unit circuits in the circuit, the relevant components in some unit circuits are often drawn messy, some are not common drawing methods, and some are individual components. It is far away from the unit circuit. In this way, part of the wiring in the circuit is very long and twisted, which makes it difficult to recognize the diagram and understand the working principle of the circuit.
6. Printed board diagram
Printed board diagram, also known as PCB diagram, printed circuit diagram, PCB layout diagram, is an assembly diagram of actual electronic components. The printed board diagram has the following two functions: â‘ According to the printed board diagram, you can easily produce a printed circuit board; â‘¡According to the printed board diagram, you can easily find the specific location of the components on the printed board. To facilitate maintenance.
Due to the complicated wiring of printed board diagrams, it is difficult for general staff to see the signal flow and working principle of the circuit from the printed board diagrams. Therefore, printed board diagrams are generally rarely used in the maintenance of liquid crystal displays.
ConclusionThis is the end of the relevant introduction about Samsung 788DF. Please correct me if there are any deficiencies.
Related reading recommendations: Analysis of various display panels, and recognize their advantages and disadvantages. Related reading recommendations: How to choose a good monitor and what is the color gamut of the display parameters?Household Appliances Zinc Alloy Die Casting
Household Appliances Zinc Alloy Die Casting,Surface Finish Zinc Casting,Handle Door Lock Parts,Zinc And Aluminum Casting
Dongguan Metalwork Technology Co., LTD. , https://www.diecast-pro.com