Self-driving vehicles can greatly reduce casualties in road traffic accidents. According to WHO statistics, about 125 million people in the world die of such accidents each year, and the population is mainly distributed between 15 and 29 years old. In addition, 200,000 to 500,000 people are injured. Most of the accidents occurred in developing countries, and the maturity of autonomous vehicles in these areas still has to go a long way.
In recent decades, cars have become more secure due to characteristics such as seat belts and airbags, but the number of road deaths in the United States has risen since 2014, apparently due to distractions from smartphones. Mature auto-pilot is obviously a great savior.
New progress in automatic driving
However, the recent release of the Autopilot Test Ranking in California, USA, has provided evidence that autopilot has become more secure. Waymo's vehicles traveled 4 million miles on public roads—the only accident it involved in autonomous driving was caused by people in other vehicles.
A self-driving car has superhuman perception and can brake in less than 1 millisecond, while humans need about 1 second. But if you simply ask for "better than people," this option is not far-sighted - self-driving cars will become more and more reliable.
Amnon Shashua, chief executive officer of Mobileye, a maker of automated driving technology, said that the human drive has been improved by a factor of 1,000. This is a realistic goal that drivers should pursue. And if this is done, the number of deaths per year in the United States from roads will be reduced from 40,000 to 40. In fact, even with modern security features, about 650,000 Americans have died on the road since 2000, surpassing the death toll of all wars in the 20th century (about 630,000 people).
In order to produce lower operating costs per mile, most auto-driving cars are almost certainly electric, and the environmental benefits will be apparent. Complementing the electric car will bring many upgrades, but even an electric car will still cause particulate emissions from tires and road wear.
The transformation of cars into electrification will require more electricity. UBS estimates that by 2050, European electricity consumption will increase by 20%-30%. For urban residents, the benefits are better air quality and less noise.
The effect of self-driving cars on reducing congestion is not so obvious - after all, when people built more advanced transportation networks in the past century, the roads were more crowded and the mileage was longer. If autopilot is cheap and fast, people will want to use them more. At this time, the shared car surfaced again - making more efficient use of the road space. Computer-controlled cars can be smarter in route planning, thereby increasing road capacity.
To be sure, drivers can save a lot of time once they do not have to drive. The Boston Consulting Group predicts that Americans can save a total of 30 billion hours each year in addition to finding parking spaces.
When the car was replacing the carriage, people thought that this seemingly clean trip was a good replacement for the scene of the old horse shit, but now air pollution is a big problem. Does automatic driving produce additional "side effects"?
Impact of Automotive Industry on Retail Industry
The car has changed the retail format and led to many suburban shopping malls with lots of shops and lots of parking lots. With the rise of e-commerce, electric vehicles may once again change this format. The University of Virginia Peter Norton said: "The future of Wal-Mart may be a group of teams, once again become a new possibility."
“Or you can use an auto-driving car to help arrange groceries or meals. Why are stores, restaurants, and other facilities fixed?†Chenoe Hart, an architect at the University of California, Berkeley, suggested that coffee shops or food stalls can be relocated to a central warehouse , and then move to the business district in the morning and entertainment areas. Mobile stores that sell items such as shoes, clothes, or cosmetics can regularly visit specific communities, especially when they are popular with customers.â€
Automakers are still exploring and experimenting with a model: The freight car is driven to the customer's home, and then the customer is sent a text message. After obtaining the code, the customer can enter the code and retrieve the item from the car. The low cost of self-driving cars can stimulate local production of various products, especially video. Already there are food supply services like Uber Eats, Deliveroo, Seamless, and GrubHub. China's dripping trips have also gone from walking to take-out business to achieve business expansion.
In these businesses, it is only necessary to focus on producing video in several kitchens, and then cheap autonomous delivery can be achieved.
Johann Jungwirth of Volkswagen said that another possibility is that restaurants or retailers may bear the cost of transportation to encourage customers to patronize them more. The fancy restaurant may use a self-driving car to take guests to their home and then let them enjoy a delicious dinner directly.
Retailers can provide shoppers with rides. The car network has a large amount of customer data that can be used to locate car ads. Self-driving vehicles arrive at a store or restaurant and can help you sell ads. You can also say Imagination: Work with a personal trainer on the way to the office, or let the barber come to your door.
Automated driving may trigger new social opportunities. For example, in the distribution of amusement facilities, the car network can bring people with similar interests or common friends together. Or they may work with the dating app to match people with potential objects while hitchhiking.
At the same time, automatic driving will also have corresponding negative impacts, such as infringing on the privacy of passengers, unfavorable to the elderly and the disabled, social isolation, and a decline in tobacco sales.
Self-driving car quickly hit the road, there are joy and worry
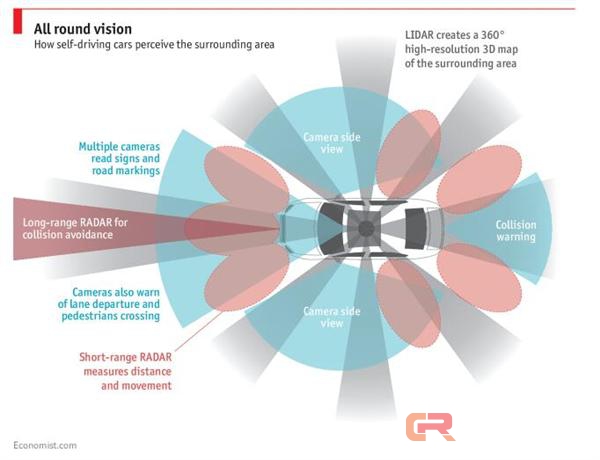
Self-driving cars use cameras, radars, and LIDAR sensors to sense the outside world. This radar-like technology uses invisible light pulses to create pleasing, high-resolution, three-dimensional maps.
About 100,000 people will ride Uber every day, and its business has expanded to more than 600 cities in 82 countries.
Currently, autopilot vehicles are not yet ready to operate without manual supervision. But in recent years, they have made rapid progress, and many cities in the United States already have self-driving vehicles on the road. Uber’s self-driving vehicles are mainly distributed in Pittsburgh and Phoenix; Waymo runs an automatic minivan in Phoenix, a suburb of Phoenix, and there is no safety engineer on the driver's seat – it plans to launch a commercial ride there; The largest automaker, General Motors, hopes to be able to introduce the automated Chevrolet Bolt in 2019 without even having a steering wheel or pedal.

Silicon Valley and Pittsburgh are two major hubs for emerging industries in the United States, attracting talents from Stanford University and Carnegie Mellon University, respectively. At CES in January this year, automatic driving can be said to steal the limelight.
The latest advances in computer vision and other machine learning systems are one reason. Technicians from chip makers to software companies have seen autonomous vehicles as a lucrative new market for their products.
At present, in rich countries, the cost of car service is around US$2.50 per mile, while the cost of owning and operating a private car is about US$1.20 per mile (see chart), but the driver accounts for about 60% of the total fare. .

UBS, an investment bank, argues that automation, competition, and electrification (making cars more expensive to buy but lower operating costs) will reduce the cost of boarding cars by 70% to about $0.70 per mile.
UBS Group’s David Lesne said: “Once a car becomes autonomous, the relevance of car ownership will fall significantly.â€
After 2025, self-driving vehicles will grow rapidly and by 2035, 80% of people will use them in cities.
The Boston Consulting Group estimates that by 2030, a quarter of the US road mileage will be shared by self-driving electric vehicles. The number of cars in urban streets is expected to decrease by 60%, emissions by 80%, and road traffic accidents by 90%.
The consulting firm Strategy Analytics stated that globally, by 2050, the “passenger economy†brought by the integration of self-driving cars and car-carrying vehicles will generate US$7 trillion in value each year.
Car manufacturers, technology giants, startups and passenger car companies are all fighting for this fiercely competitive market. Automotive manufacturers understand machine learning, but little is known about sophisticated software. These tech companies know machine learning and computer vision but don't understand cars. For those companies that like to travel by car, their applications have been installed on millions of users' mobile phones, providing a clear way for the market. The result is a series of deals, a lot of hedging bets and a changing coalition network (see chart).

In March 2017, Mobileye, an autopilot manufacturer, was acquired for $15.3 billion. In March 2016, General Motors acquired Cruise Ventures, an AV start-up company, for $1 billion, and established Maven, a car-sharing service, and invested US$500 million in Uft’s main US competitor, Lyft. Ford fired its chief executive in May 2017, partly because of concerns that the company was behind electric and self-driving cars; it is now investing $1 billion in an autopilot start-up, Argo, and has established an alliance with Lyft. Delphi, a large parts manufacturer, acquired nuTonomy, an AV start-up company, for $450 million and rebranded itself as an AV company called Aptiv. Uber recently agreed to purchase 24,000 self-driving cars from Volvo for its robot fleet; it also cooperates with Daimler. For its part, Daimler has been buying rides that compete with Uber in Europe and the Middle East and has car sharing services. VW, Europe’s largest automaker, reached an agreement with Aurora, a former executive of Google, Uber and Tesla.
Technology and automotive manufacturing complement each other and bring about tremendous changes. In the future, more and more people will consider the impact of self-driving vehicles on private mobility, car ownership, and car manufacturing, but will also consider broader economic, social, and cultural linkages—such as how daily activities will change? How does a self-driving car reshape a city? What lessons did the rise of cars in the 20th century have for the 21st century driverless cars?
Laptop Standing Desk Adjustable,Laptop Standing Desk Adjustable Height,Laptop Standing Desk Cart,Laptop Standing Desk Foldable,etc.
Shenzhen Chengrong Technology Co.ltd is a high-quality enterprise specializing in metal stamping and CNC production for 12 years. The company mainly aims at the R&D, production and sales of Notebook Laptop Stands and Mobile Phone Stands. From the mold design and processing to machining and product surface oxidation, spraying treatment etc ,integration can fully meet the various processing needs of customers. Have a complete and scientific quality management system, strength and product quality are recognized and trusted by the industry, to meet changing economic and social needs .

Laptop Standing Desk Adjustable,Laptop Standing Desk Adjustable Height,Laptop Standing Desk Cart,Laptop Standing Desk Foldable
Shenzhen ChengRong Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.laptopstandsupplier.com