Guide: Triode , as the name implies, is a pipe with three heads. What is the working principle of the triode ? Let's learn together!
1. The working principle of triode - introduction
The triode, the full name should be a semiconductor triode, also known as a bipolar transistor, a crystal triode, is a current-controlled current semiconductor device, its function is to amplify the weak signal into an electrical signal with a large amplitude value, also used as a non-contact switch. The triode is made up of two closely spaced PN junctions on a semiconductor substrate. The two PN junctions divide the monolithic semiconductor into three parts, the middle part is the base area, and the two sides are the emitter area and the collector area, and the arrangement is PNP. And NPN two. Transistors have current amplification and are the core components of electronic circuits.
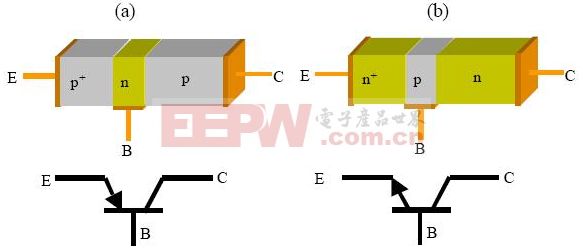
2. Triode working principle - structure
The basic structure of the triode is two reverse-connected pn junctions, as shown in the figure below, there can be pnp and npn
Two combinations. The three successive endpoints are called emitter (E), base (B), and collector (C), and the names are related to their function during triode operation. The figure also shows the circuit symbols of the npn and pnp transistors. The emitter is especially marked, and the arrow is referred to as an extremely n-type semiconductor, which is identical to the sign of the diode. When no external bias is applied, the two pn junctions form a depletion region separating the neutral p-type region from the n-type region.
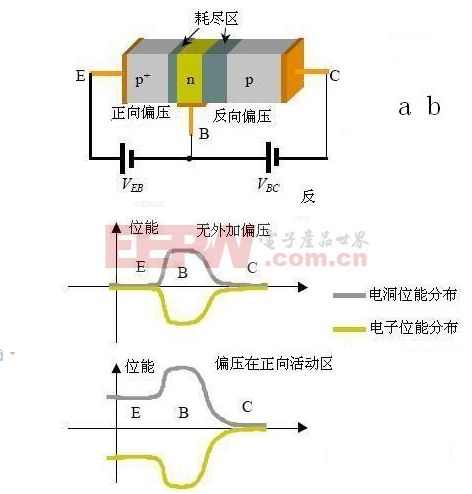
3. The working principle of the triode
Figure (a) below is a schematic diagram of a pnp transistor in this biasing region. The depletion region of the EB junction is narrowed in the forward bias, the barrier seen by the carrier becomes smaller, the emitter hole is injected into the base, and the base electron is also injected into the emitter; The depletion region of the surface is widened, and the barrier seen by the carrier becomes large, so it is not conductive. Figure (b) below shows the distribution of the potential energy of the holes and electrons in the case where the bias is not applied and the bias voltage is in the positive active region.
What is the difference between a triode and two reverse-connected pn diodes? The biggest difference between them is that the junctions of the triodes are quite close. Taking the above-mentioned bias voltage as a pnp transistor in the positive active region, the emitter hole is injected into the n-type neutral region of the base, and is immediately surrounded by most carrier electrons, and then diffused toward the collector, and is also electronized. complex. When the uncompressed hole reaches the depletion region of the BC junction, the electric field in this region is accelerated to sweep into the collector. The hole is the majority carrier in the collector, and the drift current reaches the external connection. An ohmic junction forms a collector current IC.
Expand reading:
Triode clamp works
Basic knowledge and working principle of triode
How the triode works
cell phone battery
Ethernet Keystone Jacks,Keystone Jack Inserts,Cat6 Keystone Jack,Cat5e Keystone Jack
Chinasky Electronics Co., Ltd. , https://www.chinacctvproducts.com