Analytical method
When the substance to be tested is sublimated, vaporized, decomposed or lost in the heating process, the mass of the substance to be measured changes. At this time, the thermogravimetric curve is not a straight line but a decrease. By analyzing the thermogravimetric curve, it is possible to know how many degrees the measured substance changes, and according to the weight loss, it is possible to calculate how much material is lost (such as crystal water in CuSO4·5H2O). From the thermogravimetric curve, we can know that the five crystal waters in CuSO4·5H2O are removed in three steps. Through TGA experiments, it is helpful to study the changes in crystal properties, such as physical phenomena such as melting, evaporation, sublimation and adsorption; it also helps to study the chemical phenomena of substances such as dehydration, dissociation, oxidation and reduction. Thermogravimetric analysis can generally be divided into two categories: dynamic (warming) and static (constant). The curve obtained by the thermogravimetric test is called the thermogravimetric curve (TG curve), and the TG curve is represented by the mass as the ordinate, and the mass is reduced from the top to the bottom; the temperature (or time) is the abscissa, and the temperature is represented from the left to the right ( Or time) increase.
How folding works
The thermogravimetric analyzer is mainly composed of a balance, a furnace, a program temperature control system, and a recording system.
There are two principles for the most common measurements, the displacement method and the zero method. The so-called displacement method is based on the relationship between the inclination of the balance beam and the mass change, and the inclination is detected by a differential transformer or the like, and is automatically recorded. The zero method uses the differential transformer method and the optical method to measure the inclination of the balance beam, and then adjusts the current of the coil installed in the balance system and the magnetic field, so that the coil rotates to restore the inclination of the balance beam, which is called the zero position method. Since the force applied by the coil rotation is proportional to the mass change, this force is proportional to the current in the coil, so it is only necessary to measure and record the change in current to obtain a curve of mass change.
Folding factors
Folding sample volume and sample dish
The weight of the sample is determined by the thermogravimetry method, generally 2~5mg. On the one hand, the sensitivity of the instrument balance is very high (up to 0.1 μg). On the other hand, if the sample volume is large, the mass transfer resistance is larger, the internal temperature gradient of the sample is large, and even the thermal effect of the sample causes the sample temperature to deviate linearly. The temperature is programmed to change the TG curve, and the finer the particle size, the better the sample is to be flattened as much as possible. If the particle size is large, the decomposition reaction will shift to a high temperature.
The material of the sample dish is required to withstand high temperatures and is inert to the sample, intermediate product, final product and atmosphere, ie, it has no reactivity and catalytic activity. The sample vessels commonly used are platinum, ceramic, quartz, glass, aluminum, and the like. In particular, different samples should be sampled with different materials, otherwise the sample can be damaged. For example, sodium carbonate reacts with SiO2 in quartz and ceramics to form sodium silicate at high temperature, so it is like sodium carbonate. For alkaline samples, do not use aluminum, quartz, glass, or ceramic sample vessels. Platinum sample vessels are active against hydrogenated or dehydrogenated organics and are not compatible with polymer samples containing phosphorus, sulfur and halogens.
Folding heating rate
The faster the temperature rise, the more severe the temperature lag, such as polystyrene decomposing in N2, when the degree of decomposition is 10%, the temperature is 1 °C / min is 357 ° C, measured at 5 ° C / min is 394 ° C phase difference 37 °C. The heating rate is fast, the resolution of the curve is lowered, and some intermediate products are lost. For example, some intermediates of step-by-step water loss can be detected by slowly heating the aqueous compound.
Folding atmosphere effect
The change of atmosphere around the thermobalance has a significant effect on the TG curve. The TG curve of CaCO3 in vacuum, air and CO2 has a decomposition temperature of nearly 600 °C, because CO2 is a decomposition product of CaCO3, and the presence of CO2 in the atmosphere inhibits CaCO3. The decomposition causes the decomposition temperature to increase.
Polypropylene in the air, there will be significant weight gain at 150 ~ 180 ° C, which is the result of oxidation of polypropylene, there is no weight gain in N2. The gas flow rate is generally 40 ml/min, and the large flow rate is advantageous for heat transfer and overflow gas diffusion.
Folding volatiles condensation
The decomposition product volatilizes from the sample and tends to condense again at low temperature. If it is condensed on the hanging wire sample dish, the measured weight loss result will be low, and when the temperature is further increased, the condensate will volatilize again to produce false weight loss. , the TG curve is deformed. The solution is generally to increase the flow rate of the gas so that the volatiles leave the sample vessel immediately.
Folding buoyancy
The buoyancy change is caused by the thermal expansion of the gas around the sample, so that the relative density decreases, the buoyancy decreases, and the sample is apparently weighted. For example, the buoyancy at 300 ° C can be reduced to half of the buoyancy at normal temperature, and can be reduced to about 1/4 at 900 ° C. The practical calibration method is to do a blank test (no-load thermogravimetric test) to eliminate apparent weight gain.
TG curve critical temperature representation
The temperature values ​​on the weight loss curve are often used to compare the thermal stability of materials, so how to determine and choose is very important.
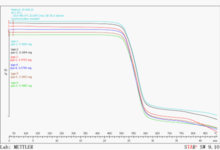
TG curve of PE of special engineering plastics research center
There is no uniform regulation yet. But for the needs of analysis and comparison, there are also some methods of identification that everyone recognizes. Point A is called the initial decomposition temperature, which is the temperature at which the TG curve starts to deviate from the baseline point; point B is called the epitaxial starting temperature, which is the intersection of the tangent line of the curve falling section and the baseline extension line. Point C is called the extension termination temperature, which is the intersection of this tangent and the maximum weight loss line. Point D is the temperature at which the TG curve reaches the maximum weight loss, called the termination temperature. E, F, and G are the temperatures at which the weight loss rate is 5%, 10%, and 50%, respectively. The temperature at which the weight loss rate is 50% is also called the half-life temperature. Among them, the temperature repeatability at point B is the best, so the temperature at which this point is used indicates the stability of the material. Of course, there is also the use of point A, but this point is generally difficult to determine due to many factors. If the tangential section of the TG curve is sometimes difficult to draw, the US ASTM stipulates that the intersection of the line between 5% and 50% and the extension of the baseline is defined as the decomposition temperature; the International Bureau of Standards (ISO) stipulates that the weight loss is 20%. The intersection of the line with 50% two points and the extension of the baseline is defined as the decomposition temperature.Evaluation of thermal stability of polymers
The easiest and most convenient way to evaluate the thermal stability of a polymer is to make TG curves for different materials and compare them on a single plot. The thermogravimetric curves of the five polymers were measured on the right. As can be seen from the figure, PMMA, PE, and PTFE can be completely decomposed, but the thermal stability increases sequentially. The stability of PVC is poor. The first stage of weight loss is de-HCl, which occurs at 200~300 °C. After dehydrochlorination, conjugated double bonds are formed in the molecule, and the thermal stability is improved (the TG curve decreases slowly) until the higher temperature is about 420. At °C, the macromolecular chain breaks, forming a second weight loss. The low decomposition temperature of PMMA is caused by the easy breakage of the bond between the tertiary carbon and the quaternary carbon atom in the molecular chain. PTFE is because the CF bond bond energy in the chain is large, so the thermal stability is greatly improved. Polyimide PI has a large amount of aromatic heterocyclic structure, and it needs to be decomposed by about 40% at 850 ° C, and has thermal stability.
Folding analysis application
The important feature of the thermogravimetric method is that it is highly quantitative and can accurately measure the mass change and the rate of change of the substance. It can be said that as long as the weight changes when the substance is heated, the thermogravimetric method can be used to study the change process. The properties measured by thermogravimetry include corrosion, pyrolysis, adsorption/desorption, solvent loss, oxidation/reduction, hydration/dehydration, decomposition, black smoke, etc., which are widely used in plastics, rubber, coatings, pharmaceuticals, etc. Research and development, process optimization and quality monitoring in various fields such as catalysts, inorganic materials, metal materials and composite materials. These include: thermal decomposition of inorganic substances, organic substances and polymers; corrosion of metals by various gases at high temperatures; solid state reactions; calcination and smelting of minerals; distillation and vaporization of liquids; pyrolysis processes of coal, petroleum and wood Determination of moisture content, volatile matter and ash content; sublimation process; dehydration and moisture absorption; study of explosive materials; study of reaction kinetics; discovery of new compounds; adsorption and desorption; determination of catalytic activity; determination of surface area; oxidation Studies on stability and reduction stability; studies on reaction mechanisms.
Folding analysis
The sample is placed at a programmed temperature and the mass of the sample is observed as a function of temperature or time. It is widely used in research and development, process optimization and quality monitoring in various fields such as plastics, rubber, coatings, pharmaceuticals, catalysts, inorganic materials, metal materials and composite materials.
The change in weight of the substance is measured (temperature changes in a controlled atmosphere). All Setaram balances meet the highest standards of accuracy and stability. Properties measured by thermogravimetric analyzer (TGA) include corrosion, pyrolysis, adsorption/desorption, solvent loss, oxidation/reduction, hydration/dehydration, decomposition, black smoke, etc.
Instrument features:
Temperature range: RT ~ 1000 °C
Heating and cooling rates are fast.
Effective accuracy: 1μg (internal accuracy: 0.1μg)
Vacuum sealed structure.
The sample temperature was measured directly.
The top loading design makes it easy to operate.
Easy to use in combination with infrared (FTIR), gas phase mass spectrometry (QMS), pulsed thermal analysis (PulseTA) and gas phase analysis (GC).
Provide c-DTA (Computational DTA) function (optional)
Super-Res (rate control quality change) function (optional)
Autosampler System ASC (optional)
TG 209 C thermogravimetric experiment procedure
Weigh the appropriate weight sample in the bowl.
Open the lid - load the sample å©åŸš - close the lid
Conditions such as temperature program and atmosphere are set in the software.
Initialize working conditions, such as gas flow, vacuum, etc.
Start measuring.
After the experiment, the raw data was analyzed using NETZSCH - Proteus software.
Source Factory Laptop Stand, Desktop Lapotp Stand in China, Desktop Holder Cooling Stand, Laptop Stand Folding Desktop, Desktop Adjustable Laptop Stand. Shenzhen Chengrong Technology Co.ltd is a high-quality enterprise specializing in metal stamping and CNC production for 12 years. The company mainly aims at the R&D, production and sales of Notebook Laptop Stands and Mobile Phone Stands. From the mold design and processing to machining and product surface oxidation, spraying treatment etc ,integration can fully meet the various processing needs of customers. Have a complete and scientific quality management system, strength and product quality are recognized and trusted by the industry, to meet changing economic and social needs .

Nulaxy Desktop Laptop Stand,Best Desktop Laptop Stand,Desktop Laptop Stand Adjustable
Shenzhen ChengRong Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.dglaptopstandsupplier.com