The English name of the ZFS file system is Zettabyte File System, also known as Dynamic File System, which is the first 128-bit file system. Originally a file system developed by Sun for the Solaris 10 operating system. As part of the OpenSolaris open source initiative, ZFS was released in November 2005 and is known by Sun as the ultimate file system for 10 years of active development. The latest development will be fully open and renamed OpenZFS
Debian in a broad sense refers to a cooperative organization and its works dedicated to the creation of a free operating system. Because many of the kernel branches of the Debian project are based on the Linux macro kernel, and most of the basic tools in the operating system created by Debian developers come from GNU projects, so "Debian" is often referred to as Debian GNU/Linux.
The unofficial kernel branch also has Debian GNU/Hurd (Hurd microkernel) that only supports x86, and only supports Dyson (OpenSolaris mixed kernel) of amd64. These unofficial branches have some serious problems, and there is no practicality. For example, the Hurd microkernel is technically immature, and Dyson's basic functions are still not perfect. "Debian" is officially pronounced /ˈdɛ.bi.ən/, and Debian is an international collaborative project. The official does not specify any non-English name.
The English name of the ZFS file system is Zettabyte File System, also known as Dynamic File System, which is the first 128-bit file system. Originally a file system developed by Sun for the Solaris 10 operating system. As part of the OpenSolaris open source initiative, ZFS was released in November 2005 and is known by Sun as the ultimate file system for 10 years of active development.
ZFS is based on storage pools. Unlike traditional file systems that map physical storage devices, all ZFS file systems in the storage pool can use the resources of the storage pool.
ZFS uses the concept of a "storage pool" to manage physical storage space. In the past, file systems were built on top of physical devices. To manage these physical devices and provide redundancy for data, the concept of "volume management" provides a single device image. But this design adds complexity and at the same time does not make the file system move to a higher level because the file system cannot cross the physical location of the data. ZFS completely abandons "volume management", no longer creates virtual volumes, but concentrates all devices into one storage pool for management! The Storage Pool describes the physical characteristics of the storage (the layout of the device, the redundancy of the data, etc.) and acts as a dedicated storage space that creates the file system. Since then, file systems are no longer limited to separate physical devices, and file systems also allow physical devices to share their own file systems into this "pool." You no longer need to pre-plan the size of the file system because the file system can automatically grow in the "pool" space. When adding new storage media, all file systems in all "pools" can immediately use the newly added space without additional operations. In many cases, the storage pool acts as a virtual memory. (The above are all taken from Baidu Encyclopedia) ZFS is divided into two parts: storage pool and file system. All ZFS file systems reside in the storage pool. The zpool command is used to manage the storage pool. The zfs command is used to manage the zfs file system.
From the above, ZFS is the default file system of Solaris. The default is no ZFS file system in Linux system. Therefore, the zpool command and the zfs command are not recognized in Linux, but the Linux system can pass the user space file system or a native third party. Kernel loading core module support.
Since the license is not compatible, ZFS has been unable to enter the Linux kernel. ZFS is distributed using the CDDL (Common Development and Distribution License) protocol, while the Linux kernel uses the GPL2 protocol. Because of the conflict between these two protocols, ZFS cannot enter the kernel main line. Although you can't enter the kernel, there is still a way to port ZFS natively to the Linux platform, which is to run ZFS as a kernel module. This is the ZFS on Linux project. ZFS on Linux was developed by the US Department of Energy, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL). ZFS on Linux only supports 64bits platform, including two components SPL (Solaris Porting Layer) and ZFS, the current version is 0.6.0-rc8, the supported zfs pool version is 28, and the file system version is 5.
$ su -
# apt-get installlsb-release #
Wgethttp://archive.zfsonlinux.org/debian/pool/main/z/zfsonlinux/zfsonlinux_6_all.deb (this command is to get the zfsonlinux_6_all.deb package)
# dpkg -i zfsonlinux_6_all.deb (install zfsonlinux_6_all.deb package)
# apt-get update (update system package file)
# apt-get installdebian-zfs (install zfs)
Because you need to connect to archive.zfsonlinux.org, you need to have an external network. The following figure shows the steps to modify IP in debian.
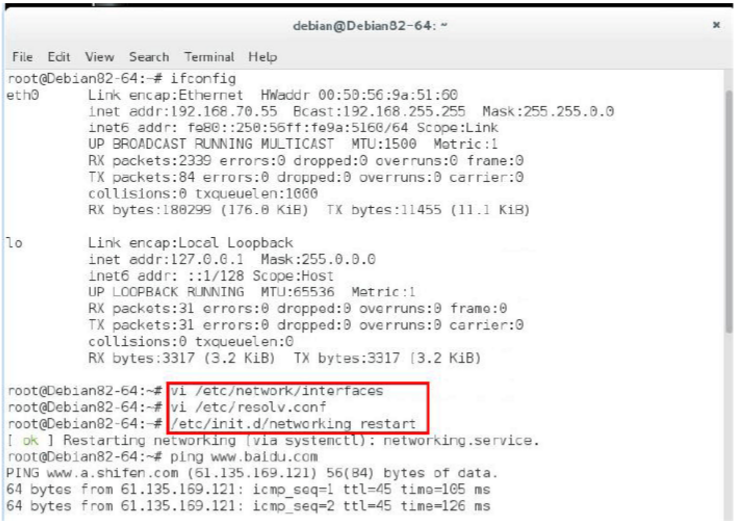
When installing debian-zfs, you will need debian8.2 iso in the middle. As shown below, you can put ISO in advance, or insert ISO when prompted to do the following, and press Enter. ISO is our system ISO DVD1. .

When installing debian-zfs, you will need debian8.2 iso in the middle. As shown below, you can put ISO in advance, or insert ISO when prompted to do the following, and press Enter. ISO is our system ISO DVD1. .
At this point, the Linux system can already support the ZFS file system. Let's start by creating a storage pool.
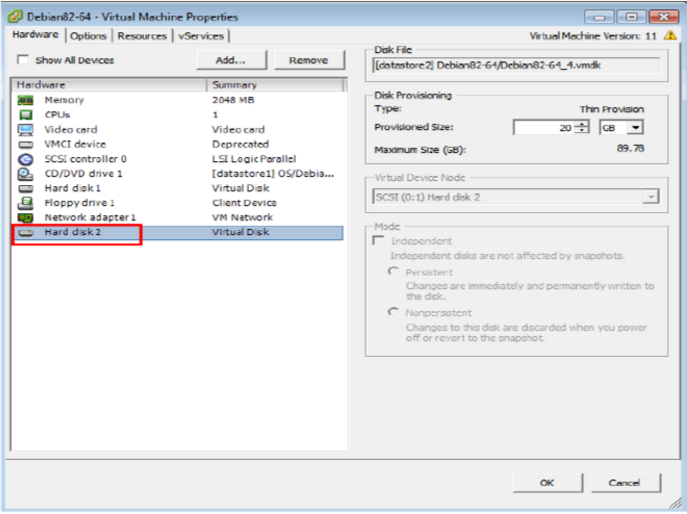
You can use a single disk, a partition or file on a disk to create a ZFS storage pool, but it is recommended to use a single disk to create a storage pool, and it is best not to use virtual volumes provided by hardware RAID. So we add a new hard disk to create a storage pool, which can be added by editing -> settings, size is not required:
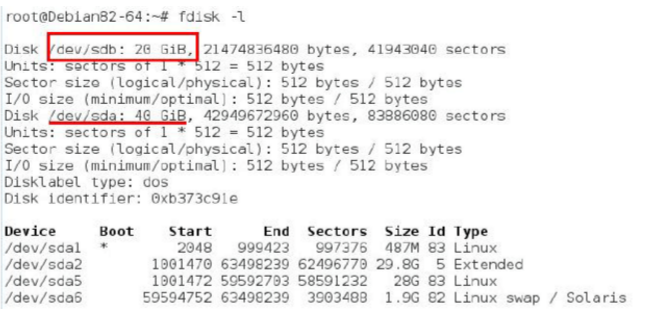
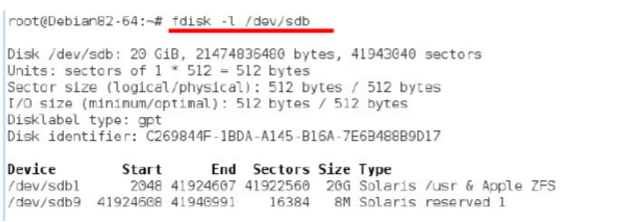
The disk information can be viewed through fdisk–l, as shown below: sdb is the newly added hard disk. If you enter this command after adding a new disk and you don't find sdb, it is because adding a new hard disk requires restarting the machine, and you can find it after rebooting.
# zpool create -f reservoir /dev/vdb /dev/vdc /dev/vdd These are the names of the three hard drives, and reservoir is the name of the storage pool. If you do not specify the mount point with the -m option when creating a storage pool, the pool will be mounted to the /poolname directory by default, so the storage pool created at this time will be automatically mounted to /reservoir, and ZFS will automatically start at boot time. Mount the storage pool.
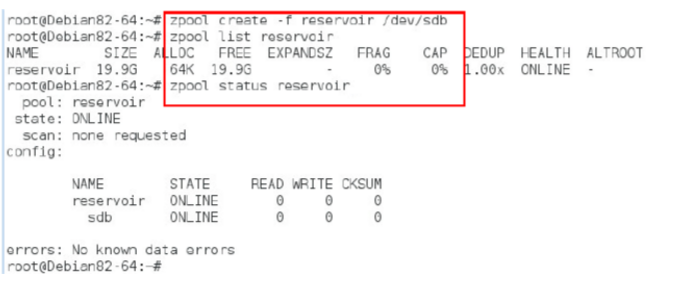
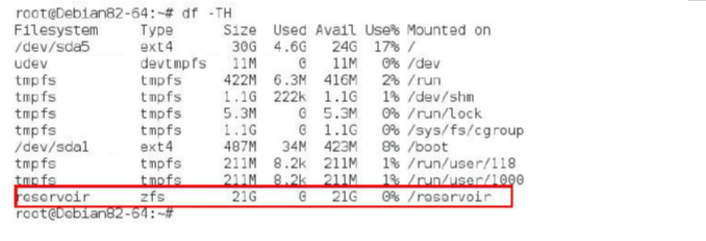
Here is the storage pool repository and ZFS file system. You can create a new ZFS file system in the storage pool: # zfs create pool-name/[filesystem-name/]filesystem-name (eg: #zfs create reservoir/data) You can also specify a mount point:
# zfs create -o mountpoint=/mnt/data reservoir/data
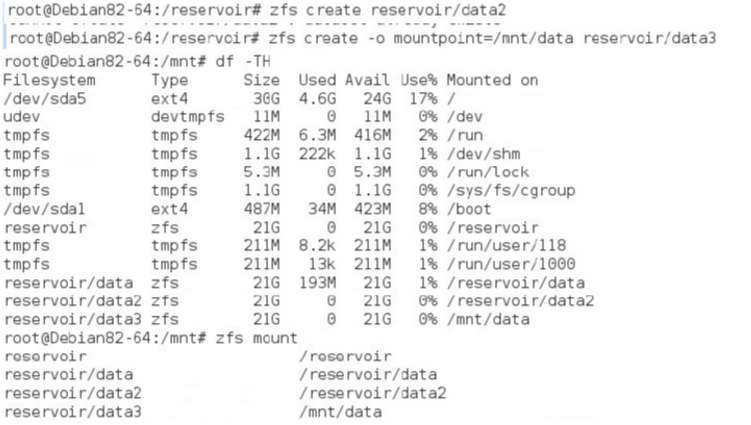
The introduction of ZFS file system installation in debian has been completed, you can also try some other features of ZFS.
Stainless Steel Pressure Gauge For Marine
High performance silicon piezoresistive pressure core is adopted to maintain the characteristics of solid-state sensor. The intelligent microprocessor is adopted to eliminate the adjustment of movable parts, so that the digital Pressure Gauge has a longer service life. LCD digital display avoids the error caused by analog display instrument in the reading process. The zero adjustment of the display value can be completed only through the button on the panel.
The reading shows that it will automatically enter the sleep working state after a period of time, and the power consumption of the pressure gauge is very low. The excellent accuracy and convenient reading make jb500 pressure gauge an ideal upgrade substitute for traditional analog pressure gauge.
Stainless Steel Pressure Gauge For Marine,Digital Pressure Gauge,Oxygen Pressure Gauge,Stainless Steel Shockproof Pressure Gauge
Taizhou Jiabo Instrument Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.taizhoujiabo.com