Of course, everyone is referring to this phenomenon as a "sounder". Then take the Epos 11's manual and see that its low-frequency response is only 75Hz. This is consistent with the author's previous perception that the depth is about 50Hz. The contradiction has led to the experiment we have re-explored, and we decided to test it with frequency.
Experiment with CD test piece
The experiment was divided into two times, and the test CD (TES-1000) was used as the sound source. The only ones present were Jun Mingxiong, Jin Leixiong and the author. The equipment is as follows:
CD turntable: Thorens "TCD-2000" CD turntable
D/A Converter: Sonic Fronfiem "SFD-2II" Digitizer Preamplifier: Audio Research "LS-8II" Preamplifier: KreH "KSA-300S" Enlarger Speaker: Cdefion "SL-12 "Two-way three-unit horn signal line, speaker line and CD to D/A line are all Siltech sterling silver wire. We listen to a single frequency, from low to high, 16Hz can't hear it at all. At 25Hz, the speaker has The bass is not quite right, then listen to 32Hz, and the results are listed as a table:
The 32 Hz sensor sound spreads the widest, deepest, the deepest vocalization point and the lowest vocalization position.
The 125 Hz vocalization point moves slightly forward, the width is slightly reduced, the lighter, and the position is slightly higher. The sound point moves forward again, narrower, shallower, and slightly higher.
The 250Hz sounding point seems to be forward, narrower and higher.
The 500 Hz vocalization point is no longer forward, but it is a little higher and the top begins to widen.
The 1KHz vocalization point is later retracted, but the above spreads wider.
The 2KHz sounding point is more retracted, the position is higher, the spread is wider and larger.
4KHz has the pressure from the head down, the position sounds higher, and the top is wider.
The 8KHz head feels less, the sound is higher, and the back is bigger.
16HHz can't hear too much.
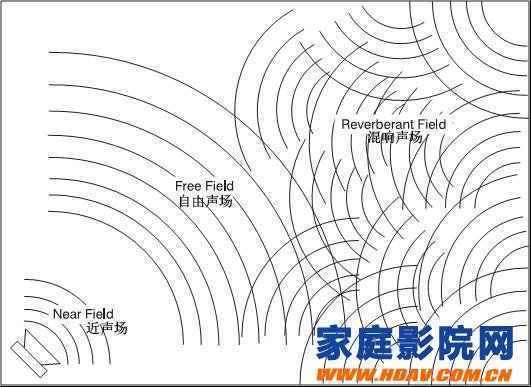
This time, I heard that the feeling brought by a single frequency does have different heights, widths, and differences. At the same time, high frequency has the feeling of sounding at high places, low frequency has the feeling of sounding at low places, and higher frequency. And the lower frequency is more diffuse, but the intermediate frequency does not spread, it seems that the focus is from the intermediate frequency in the tube, roughly the low-frequency tube depth, the high-frequency tube height is not wrong, and the frequency tube width of 100Hz, 120Hz is considered. The arguments have raised doubts. On the table, you can also see that the 125Hz and 250Hz vocalization points are not wide, but they all have forwards (please refer to the simplified diagram, drawn by Jun Ming brother), which is the closest to listening. The part of the person can indicate that the front of the stage is close to the listener. Imagine a symphony orchestra moving forward. This feeling is like the closer you are to the visual thing, the wider the thing. In fact, we will pay attention to the audition equipment. The two corners on the left and right sides of the stage are full. Some people even use the pen to draw the stage is semi-circular or trapezoidal. Obviously, the rear corner of the stage is full and you have to pay attention to 32Hz. Or the lower frequency band situation; and want to create an orchestra to listen to the feeling of indoor performance, you have to pay attention to the proportion between 125Hz-250Hz and other frequency bands, this paragraph seems to control the front position of the stage. It is well known that the human ear itself responds to the frequency and is non-linear. In addition, when there are multiple frequencies appearing together, what kind of changes will happen to the human reaction. So far, no scientific discussion has been made. The author borrows human vision and taste. The tactile response is set in the sense of hearing, but it still works. In particular, people's feelings are relative. I believe that it is no exception to hearing. For example, the response of people to the cold and warmth in the sense of touch can be known by washing hands with groundwater. The temperature of groundwater is very limited in winter or summer. The daily use of groundwater to wash hands feels cold, and the cold ground feels that the groundwater is warm; a little bit of salty stuff adds a little sugar, it tastes just right, bitterness is also the case, adding sugar when drinking coffee is the best example.
Visually, you can use your home TV to experiment. The friends who have adjusted the color of TV have experience. After the yellow is turned off, the picture will appear purple. In fact, (the purple button is not adjusted), as long as the yellow is turned back, The color of the TV is normal; the red is cut off, and the whole picture is green. In fact, the green color has not increased, but the red color is missing.
This kind of relative feeling is also very well explained when used in the sound. For example, the ultra-low frequency is too heavy, the audio image becomes blurred, and the middle sound is too strong, the person feels that the bandwidth is narrowed. It is best to use the traditional Chinese medicine on the five elements of the line to see the results. Because the author has repeatedly insisted that the people inside the circle can not be extended by the theory that modern people do not understand, you can avoid the evil spirits. Since the human ear is not linear, and people's subjective consciousness often picks a certain frequency or a special kind of musical instrument as the focus of observation, these traps are usually the most difficult to get rid of our collective audition purpose when they are alone. In reducing these inevitable human factors. Under this premise, I decided to do another experiment.
Experiment with a signal generator
Jin Lei happened to have something on the day, and the younger brother, Jun Ming, had already made an appointment, and proposed to use the signal generator to avoid the frequencies on the CD (plus the influence of CD players and D/A converters).
The equipment for the second audition is the same as the previous one, except that the CD part is omitted and the signal generator is used as the sound source. When the signal generator is used, the frequency can be continuously adjusted, which is much more convenient. We still listen to the high sound from the bass according to the previous method. When I hear 1KHz, the problem comes out. Some frequencies are loud in the same position, and some frequencies are different in different positions.
I decided to adjust the position of the horn with music first, listened to it with Stereo once, and then moved the horn to the middle to listen to only one horn. The younger brother of the theory did not agree, thinking that the problem of the size should be clarified first.
To be honest, I also think that is more reasonable, but in fact an ideal experimental environment is not something I can afford, let alone our purpose is to observe the direction of the sound in the general listening room, not scientifically. The discussion paper, coupled with the valuable time of the participants, does not try at this moment and does not know which year to get the soundless room, the volume can be controlled slightly. Welcome to the home theater network decoration network!
What Stereo heard can provide us with a review of the usual audition. MONO heard that we may understand the difference in height, depth and width of different frequencies. As for why some frequencies become louder, is it because the room is still an audio stand? The shelf or the marble slab, the upper cover, and even the filature are reserved for later play. We only talk about the part that can reach a consensus between 15KHZ and 30HZ (and then the low-frequency horn is not).
The sound position of 30Hz is still the lowest, and the deepest is spread toward the back of the horn, and the sounding area is a large blur.
The 40Hz sounding position is slightly higher, the sounding position is also blurred, but the range is small, moving forward slightly, and also spreading toward the horn, not so deep and not so full.
The 50Hz sound source sounding area is also unclear, slightly higher, the sounding area is smaller, but also scattered backwards, but the range is smaller.
The 60Hz sound source is slightly smaller than the former, and it is forward, and the volume is higher. It is considered to be a high current relationship, and the situation of diffusion to the rear of the speaker is lowered.
The 80Hz has a tendency to spread forward, and the eight-shaped opening with a large opening spreads to the listening place, and the sound source is slightly smaller than the former.
100Hz is also forward-spreading, and the figure of the figure-eight is narrower. The source is at the speaker.
The 125Hz sound source and the reflected sound are very average, and there is also a reflection sound behind the listener. The sound source is near the speaker, and the height has risen to a position slightly lower than the speaker.
The 200Hz sound source is between the horn and the back wall, and the height is as high as the horn, and the feeling of forward diffusion is obvious.
The 250Hz fan spreads forward, and the sound source is clear and slightly higher at the back wall.
The 500Hz sound source rises and the sound is on the speaker panel.
It is worth noting that 80Hz and 100Hz have a figure-eight diffusion. The 250Hz fan has a fan-shaped spread to the bottom of the listener. Below 50 Hz, there is a feeling of diffusion toward the rear of the horn. The lower the grading, the more the scatter is, and the larger the range is. The 125HZ and 200Hz sounds are the closest to the diffuse sound (reflected sound). The 250Hz sounding position is at the back wall of the horn. The 500Hz sound is placed on the speaker cone.
Maybe you think that before you buy a horn, you should look at the spectrum measured by the horn in the sound room. That's right, but you should pay attention to where you put the horn in the room and how it reflects. Of course, the frequency at which the room has a standing wave is to be noted. If you know more about the sound, you will naturally use the position method to reduce the rendering of the standing wave. (It is definitely not worthwhile to build a house without a standing wave).
The sound source above 500Hz is raised upwards, the 2KHz audio image is the most coherent, and the 1.5KHz audio image is relatively loose. The 4KHz audio image began to expand upwards until 7KHz became a large piece on the top and closer to the listener's head. At 7.5KHz, there was a pressure from the top of the head. 7.9KHz seems to be on top of the head, 8KHz even moving in the direction of the back brain. , up to 10KHz.
11KHz began to widen, no go to the back of the brain, the height is unchanged, 12KHz width is narrow, almost the same width as the ear, slightly higher, to 13KHz feeling is narrower and higher, from the front through the head facing the rear, 14KHz today listener I felt that the sound came out from the front direction and spread out in a radiation pattern, feeling that there was music behind it. 15KHz is more open, higher, wider and deeper. In addition to the back of the horn, there is depth in the rear of the listener.
Above 10KHz, the volume of the sound is different in different positions in the room. The sound around 8KHz has the feeling of pressing top. 14KHz and 15KHz create a lot of sense of space. It can reach the rear of the listener and has a large radiation spread. It is obviously high. The frequency part is closely related to the size of the sound field. The ultra-low frequency also has the spread of the full room running. Of course, this test is to test the human ear's reaction with a single frequency. The music is extremely complicated and various frequencies appear together. The situation is much more complicated.
The high-frequency expansion is not good, it seems that it is not only known by the sense of height, but the sound field is not too big and seems to be worthy of reference. The sense of depth (referred to as the rear of the stage) and the subwoofer that I used to read is very intimate. This time I found out that it has something to do with UHF. Most of the sounds from the instruments are on the stage. The realism of the stage is inextricably linked to the frequency below 40Hz. Most of the low-frequency instruments are placed deep in the stage. The subwoofer has a problem, and the stage is not right. .
Most of the super treble is overtone, and the instrument has no way to make sounds above 6KHz, they should be weak enough to be heard. After all, it is more appropriate to have a good stage to talk about a broad sound field.
With these two tests, we know that the thickness of the instrument on the stage should be created by the smooth bass. The slope of the attenuation of the ultra-low frequency without the crossover seems to be gentle, which seems to explain the depth of Eposll. The smooth midrange provides a condensed audio image, and the super high-pitched sound source makes me hear the small information coming back from the stage and around the stage, creating the sound field on the head, the wide and deep stage, tall and big. It doesn't seem difficult to create a sound, and the frequency response of a segmental flat is enough.
But apart from the sound field, what about the sound? The details of the dark part? This time, the author listened to the Victorian Philharmonic Orchestra under the command of Ozawa Seiji. The most impressive thing is the last waltz, the kind of frenzy, his own home. Can't find 30%, no wonder there is a conductor who said that what can be called music on the recorder?
in conclusion
This article only provides the reference for those who want to create a sound field. It is not an academic study. I hope that everyone can further explore the sound and correct the communication. The results of the two experiments have different places, such as 4KHz, 8KHz.
I prefer to use the signal generator, and the pressure on the top of the 8KHz is quoted by Professor Haas's paper. The truth can be copied. It is the common desire of the audio fans to flatten the frequency response curve. I hope that people of insight will speak.
The WiFi 6 Ceiling Wireless AP is a ceiling wireless access point based on the WiFi 6 (802.11ax) standard. It is a device designed to provide wireless Internet connectivity and can be mounted on the ceiling of a building to provide users with high-speed, stable wireless Internet coverage.
WiFi 6 Ceiling Wireless AP offers a number of advantages over previous WiFi standards such as WiFi 5, or 802.11ac. The benefits of WiFi 6 Ceiling Wireless aps and how they affect users are described in detail below.
1. Higher speed and capacity:
WiFi 6 Ceiling Wireless AP uses OFDMA technology (orthogonal frequency division multiple access), which can divide the wireless channel into multiple sub-channels, each sub-channel can transmit multiple data streams at the same time, improving the capacity and efficiency of the network. This means that the WiFi 6 Ceiling Wireless AP can deliver higher speeds and more stable connections to more devices at the same time with the same spectrum resources. For high-density environments, such as office buildings, conference rooms, or large event venues, WiFi 6 Ceiling Wireless AP can better meet users' needs for high-speed networks.
2. Low latency:
The WiFi 6 Ceiling Wireless AP uses Target Wake Time (TWT) technology to put devices to sleep at a predetermined time, reducing communication latency between devices. This is important for real-time applications such as video conferencing, online gaming, and iot devices. A low-latency network can provide a better user experience and support more real-time applications.
3. Better coverage:
The WiFi 6 Ceiling Wireless AP uses higher antenna gain and more advanced beamforming technology to provide wider coverage. This means that in the same environment, the WiFi 6 Ceiling Wireless AP can provide a more stable, longer distance wireless signal, reducing signal attenuation and interference, and improving network reliability and coverage.
4. Better power management:
The WiFi 6 Ceiling Wireless AP uses Target Wake Time (TWT) technology to put the device to sleep for a predetermined amount of time, reducing the power consumption of the device. This is important for battery-powered devices such as smartphones, tablets, and iot devices. Better power management can extend the battery life of the device and reduce frequent charging of the battery.
5. Better security:
WiFi 6 Ceiling Wireless AP uses stronger Encryption algorithms and authentication mechanisms, such as WPA3 encryption and Opportunistic Wireless Encryption (OWE) authentication, to provide better security protection. This is important to protect users' personal information and network data. The WiFi 6 Ceiling Wireless AP also supports more user isolation and guest management features to better protect the network.
In summary, the WiFi 6 Ceiling Wireless AP offers higher speed and capacity, lower latency, better coverage, better power management, and better security than previous WiFi standards. These advantages can provide a better user experience and meet the needs of users for high-speed, stable and secure wireless networks. Whether in the home, office or public space, WiFi 6 Ceiling Wireless AP is an ideal wireless access solution.
Wifi 6 Ceiling Wireless Ap,Access Point Ceiling Mount,Ceiling Access Point Poe Wifi 6,Wireless Mu-Mimo Gigabit Ceiling Access Point
Shenzhen MovingComm Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.movingcommtech.com