I. Introduction
MPEG-4 is a member of the Moving Picture Ex-pert Group (MovingPictureEx-pertGroup) standard family and is a solution developed by the International Organization for Standardization for multimedia communications. Today's rapidly developing interactive computer game image display and interactive video on demand (VOD) all indicate that television is developing from "purely linear" to "non-linear". MPEG-1 / 2 uses audio frames and video frames as encoding objects, and the scene composed of AV (Audio, Video) objects in the image cannot interact with people. The main feature of MPEG-4 is to encode the content in the image. The specific encoding object is the audio and video signals in the image, called AV object. MPEG-4 is formulated around the encoding, storage, transmission and combination of AV objects. Therefore, MPEG-4 is known as the standard for encoding, storing, transmitting and combining non-linear television.
2. Technical structure of MPEG-4 image and video standards
1. Technical structure of MPEG-4 image and video standards
As shown in Figure 1, the bottom layer is the VLBV (VeryLowBitRateVideo) core, which provides algorithms and tools for 5 to 64 kbit / s video operations and applications, supports lower spatial resolution (less than 352x288 pixels) and lower frame rate ( Below 15 Hz). The special functions supported by the VLBV core include real-time multimedia applications: support for efficient encoding of rectangular image sequences, with high encoding efficiency, high precision, high error tolerance, and low latency; and multimedia database applications: support for multimedia database storage and random storage Fetch and FF / FR (fast forward / rewind) and other functions and operations.
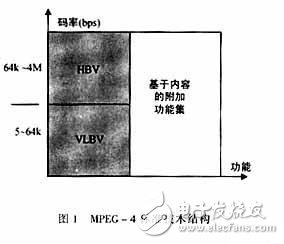
The MPEG-4 HBV (HighBitRateVideo) spatial resolution supports CIF-HDTV, with a code rate range of 64 kbit / s to 4 Mbit / s, and also supports the above functions.
Three, MPEG-4 video coding standard and MPEG-1 / 2 and its comparison with H.26X
Both MPEG-1 / 2/4 video compression and H.26X video compression technology are based on DCT (Discrete Full Cosine Transform). But they have different characteristics.
The MPEG-1 standard is an international standard mainly for digital storage media moving images and accompanying audio coding of data transmission rates below 1.5Mbps. It is used to store synchronized and color motion video signals on CD-ROM. The SIF standard exchange format (352 & TImes; 240 for NTSC and 352 & TImes; 288 for PAL) is used for image compression. It can play 30 frames per second with CD quality.
The MPEG-2 standard pursues a coding standard of 3 to 10 Mbps high-quality moving images and accompanying sounds formulated by CCIR601 for image quality DVB, HDTV, and DVD. MPEG-2 can be used to provide broadcast-grade digital video for broadcast, cable TV networks, cable networks, and direct broadcast satellite (DirectBroadcastSatellite).
The formulation of H.261 is suitable for broadband transmission on the ISDN network, which provides video coding and decoding for P & TImes; 64kbit / s audiovisual services.
H.263 is a video coding recommendation for narrow-band communication channels suitable for PSTN (Public Telephone Network). It can be used for codecs with very low bit rates for video phones. It is an important development of H.261.
The MPEG-4 standard provides a new method for communication. Its core is content-based AV information storage and operation, supporting interactivity, high compression ratio, and usable storage. At the same time, it is adaptable and extensible in structure to adapt to the rapid development of hardware and software and integrate new technologies in time. Since content and interactivity are the core of MPEG-4, the specific code rate range is no longer a special requirement, but the low code rate is still a basic content of it. .263 has certain similarities, but it also supports high-quality video and voice communications. Therefore, MPEG-4 provides a broader development platform, which is more in line with the development trend of multimedia communications and has broader application prospects.
4. Multimedia transmission system with MPEG-4 as standard
1. Scheme design
Based on the comparison of the above video coding standards and the needs of practical application, we designed a set of multimedia communication system based on Internet. The composition of the system is shown in Figure 2. It mainly includes multimedia information processing module, TCP / IP communication protocol module, communication interface module, control module, external device interface and external device module (camera, microphone, display, speaker).
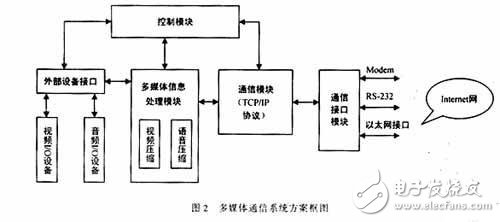
2. Functions and implementation of each module
(1) Multimedia information processing module
It is mainly based on the MPEG-4 standard, according to different application requirements for video and audio digital signals to varying degrees of compression / decompression.
1) Compression of video / audio signals
Using TI's latest TMS3206415DSP chip, it supports the 8bit data processing instructions of the image. Its calculation speed is fast, the highest running speed is up to 600MHz, the shortest instruction cycle is 1.67ns, and the peak processing speed reaches 3 200 ~ 4800 MIPS. In audio / video applications, its performance is increased by 15 times. With advanced super long instruction word structure (VLIW), it obtains the extremely high performance required by current application equipment. The 8 functional units of the core can perform 4 groups of 16-bit MAC operations or 8 groups of 8-bit MAC operations in each cycle to obtain maximum parallelism in processing communications and imaging algorithms. If C6415 is used to complete one channel of MPEG-2 video coding, one channel of MPEG-4 video coding and one channel of video decoding at the same time, its hardware resources only occupy 50%, showing its powerful computing power. The chip has a real-time hierarchical storage system with 1,056 bytes of on-chip SRAM, which is used to speed up ultra-high-speed DSP cores. The 64-channel enhanced memory direct access (EDMA) controller shows excellent parallelism characteristics. The external dual bus provides more than 1.2 Gbytes of external memory bandwidth. It also provides a 33MHz / 32 bit PCI interface and three multi-channel buffered serial ports. All of these provide convenient conditions for real-time processing of video and audio signals.
2) Video compression module
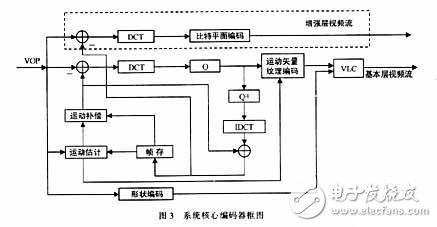
The MPGE-4 standard is adopted to achieve content-based encoding and encoding scalability. The structure of its core encoder is shown in Figure 3: The basic layer uses MPEG-4 basic mode encoding and outputs basic video streams. The enhancement layer The input signal is the difference between the original VOP and the frame stored (reconstructed) VOP, and the difference is 8 × 8 DCT, and then the DCT coefficients are bit-plane encoded. According to the importance of the bit plane, put important bits at the front of the code stream, such as the MSB of a block, and place secondary bits at the back, such as the LSB of a block, so that when the network is congested, you can discard some Important bits to slow down the network load, but the decoding end can still decode the received code stream, but the image quality will be reduced. The decoder is the inverse process of the encoder.
3) Features of video compression using MPEG-4 standard
â‘ Unification of traditional coding and content-based coding
The core of the MPEG-4 video algorithm is to support content-based encoding and decoding functions, that is, to encode and decode individual physical objects extracted using segmentation algorithms in the scene. In order to achieve the expected content and interactive functions, MPEG-4 introduced a concept called "video object plane" (VideoObjectPlane, abbreviated as VOP), as shown in Figure 4. Figure 4 (a) shows the common MPEG-4 encoder supporting MPEG-1 and MPEG-2, which regards the video image as a rectangular area, and FIG. 4 (b) shows the very low bit rate image of MPEG-4 (VLVB ) Core encoder. It is assumed that each frame of the image is divided into many objects of any shape, each object may cover the physical object or content of interest in the description scene, which is defined as VOP. Then separately encode and transmit the VOP shape, motion and texture information to form a separate video object layer (VideoObject Layer, abbreviated as VOL). In addition, the information needed to identify each VOL is also included in the encoded bitstream, and also includes information on how to reassemble the video images of various VOLs at the receiving end in order to reconstruct the complete original image sequence . This allows each VOP to be decoded individually, providing flexibility in managing video sequences.
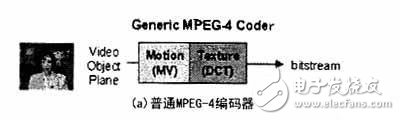
If the input image sequence contains only standard rectangular images, shape coding is not required. In this case, the coding algorithm structure used by MPEG-4Video is the same as the algorithm structure used by MPEG-1 and MPEG-2.
â‘¡ Realize continuous scalability of coding
For the application of Internet video streaming, MPEG-4 Version 4 defines the fine scalability (FGS, FineGranularityScalability) of video image coding and its implementation tools. Because FGS coding puts forward a concept that the network receiving end controls the code stream it receives, making its transmission on the Internet more adaptable.
In the hierarchical coding technology of video, the video information is divided into multiple layers of different importance, where the basic layer contains the most important basic information in the video object, so as to ensure a most basic image quality during transmission Give higher priority. The role of the enhancement layer is to further improve the image quality on the basis of the base layer, and give lower priority in transmission. In this way, when the network is congested and packet loss occurs, the enhancement layer with lower priority can be discarded first, so that the probability of packet loss or bit error in the base layer is lower than that of the enhancement layer, thus ensuring that the reconstructed image still has an acceptable quality.
4) Voice compression
Using CELP (CodeExcitedLinearPredication) code excitation linear prediction technology. The traditional CELP encoder provides a single bit rate of compression, and this system allows multiple applications to use a basic encoder, providing scalability in bit rate and bandwidth. According to the needs of different applications, two sampling frequencies of 8 kHz and 16 kHz can be selected. The sampling frequency of 8 kHz corresponds to the communication quality of 100 to 3 800 Hz bandwidth, and the sampling frequency of 16 kHz corresponds to the communication quality of 50 to 7 000 Hz bandwidth.
(2) External device interface module
This system uses the video coding chip SAA7111 of PHILIP Company, which separates the bright color of the input analog video signal of the analog camera, and then samples the separated signal by 8 bits.
Car Battery Test Pen ,Car Battery Tester ,Digital Circuit Test ,Electric Circuit Test
YINTE TOOLS (NINGBO) CO., LTD , https://www.yinte-tools.com