The network structure of cellular mobile communication can be roughly divided into terminals, base stations, base station controllers and MSCs. The interface between them is called Um, Abits, and A interface. Any problem with any network element or interface can cause a wireless network failure. A wide range of antenna feeder systems, repeaters, towers, a variety of wireless fading environments, an amazing number of Abit2MB interfaces and CIC circuits, and dazzling mobile terminals make it difficult to find wireless network faults. Here, "accurate positioning, rapid strike" is not a "surgical" military strike, but the dream of mobile communications "special forces" (operation and maintenance and network optimization communications engineers). This article will show you how to use the instrument at hand to find complex wireless network problems through several practical cases.
2 equipment"If you want to do something good, you must first sharpen your tools." For operation and maintenance and network optimization communication engineers, the necessary test equipment is necessary to solve complex problems. The following instruments are "equipments" that are often used.
(1) Mobile phone comprehensive tester R&SCMU200. Used to test handset RF and protocol performance. It can simulate base station, BSC, switching network element, can set wireless network parameters, support GSM/(E)GPRS, CDMA/EV-DO, WCDMA/HSPA signaling test.
(2) Audio Analyzer R&SUPV. Used to test the audio performance of your phone. GSM, WCDMA, CDMA mobile phone audio test software can simultaneously generate 2 channels of 0~200kHz single or multi-tone signals, simultaneously analyze 2 channels of 0~250kHz audio signals, directly display audio frequency, level, THD, SINAD, etc. index.
(3) Handheld multi-function spectrum analyzer R&SFSH. Used for spectrum, antenna feeder testing and interference finding. Supported test items include VSWR test, breakpoint test, GSM, WCDMA, CDMA channel power test, spectrum analysis, gain test, and interference test.
(4) Road test software R&SROMES+ sweeper R&STSMx. Used for network coverage testing and interference finding. Control multiple test phones and scanners. Support GSM/(E)GPRS, CDMA/EV-DO, WCDMA/HSPA network, can directly output GSM same, adjacent frequency interference cell, GSM, CDMA, WCDMA missing neighbor cell, pilot pollution number, real-time Layer3 message.
3 actual cases3.1 Case 1
(1) Problem: Multiple GSM mobile phones display "unregistered SIMCard" after being turned on locally in the morning, and the SIMs in these mobile phones can work normally before being turned on. After the SIM card is changed to another mobile phone, the fault remains, but the card reader reads the SIMCard user information normally.
(2) Analysis: HLR missing IMSI information, network blocking, SIM card problems, will lead to registration failure. Finding this problem requires coordination across departments and is a lot of work. But we cleverly used the road test software ROMES and the mobile phone tester CMU200, and quickly found the fault by tracking the phone's Layer3 message on the spot.
(3) Method: Put the SIM card to be tested into the GSM test mobile phone controlled by the ROMES software, start up in the current network environment, try to register, and record the Layer 3 message that the mobile phone registration failed in real time (see Figure 1). Connect the shield box to the RF port of the CMU200 and test the phone into the shield box (see Figure 2). Set the CMU200 to work in the GSM900 band, without authentication, and the parameters are common settings. Turn on the power and close the shielding box. At this time, only the signal transmitted by the CMU200 exists in the shielding box. The mobile phone still cannot be registered, and the status is unchanged. Therefore, the device or parameter reason above the Abits port can be excluded. After replacing the original SIM card with a standard test card, the same operation is repeated, and after successful startup, the ROMES records the Layer 3 registration message of the test phone in real time (see Figure 3). Usually the process of registering the phone should be like this (see Figure 4):

Figure 1 failed location update message

Figure 2 CMU200 and shielded box connection test mobile phone

Figure 3 Successful Location Update Message
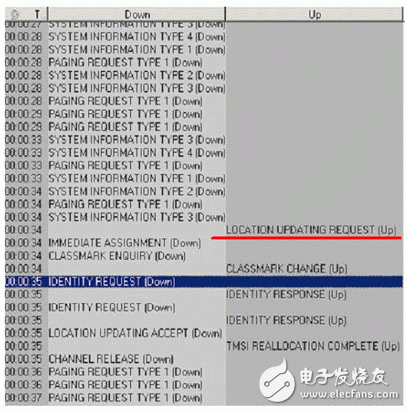
Figure 4 GSM mobile phone boot registration process

Figure 5 audio analyzer and CMU200 test mobile phone audio performance

Figure 6 uses ROMES plus TSMx to find interference
After the phone is turned on, it first searches for the frequency of the last shutdown SIM card storage. If it cannot be found, it will find the strongest signal in the entire supported GSM band. After the frequency is locked, the synchronization and reception system messages are completed. The handset then initiates the IMSI configuration procedure, notifying the system that it is in an active state.
There are two ways for a mobile phone to initiate an IMSI procedure: IMSI authentication or TMSI and LAI authentication. When the mobile phone is activated for the first time, the mobile phone is transferred to another PLMN area, and the mobile phone moves to another VLR and VLR that has just been reset to delete the data of the mobile phone, the IMSI authentication method is used, that is, the mobile phone is required during the registration process. The IMSI is transmitted to the MSC.
Stainless Steel Decorative Tube
ShenZhen Haofa Metal Precision Parts Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.haofametals.com