Press: It seems a bit late to write motion tracking technology 101, but still want to write, because the tracking technology of VR often sees a variety of mixed, so that people are puzzled. This article attempts to clarify some of the basic theories and techniques of tracing, which are already well understood by various industry players.
At this year's I/O conference, Google introduced the official helmet design reference for the Daydream VR platform, and included a handle. About this handle, many foreign media (such as The Verge) call it "MoTIon Controller", which means it can capture your movements and let you operate by gestures. However, when Xiao Bian called it the "moving handle", the industry said that "this is not a catch, and Google did not call it a catch."

So, is the Daydream handle moving? In fact, you can call it a “moving handleâ€, but you need to understand that it is different from other products. Let's take a look at how the interception should be understood.
6 degrees of freedom (DOF)
To understand the Daydream handle, you must first understand the "degree of freedom". This is a word you often hear. The English name is "Degrees of Freedom, usually abbreviated as DOF".
Freedom refers to the basic movement of objects in space, a total of six. Any sport can be split into these six basic movements. These six basic modes of movement can be divided into two categories: displacement and rotation.
The displacement includes front, back, left and right, and up and down, as shown in the following figure.
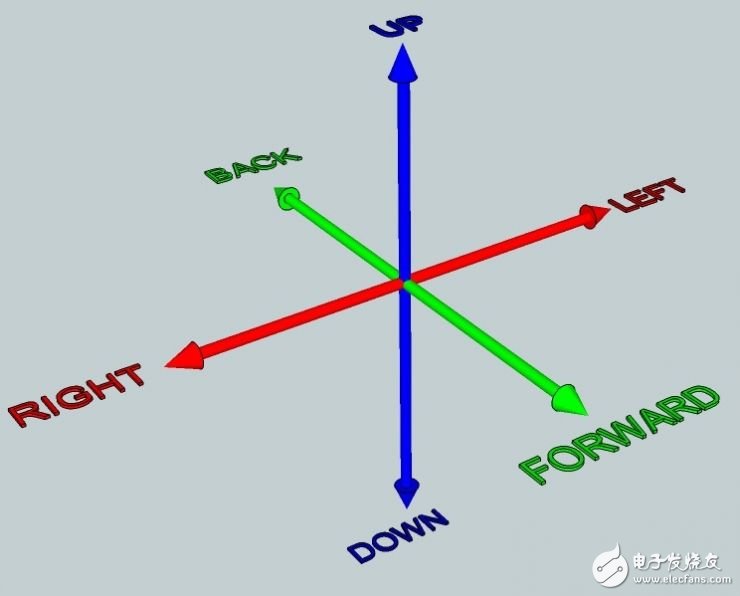
Rotation includes: front and back flip (ROLL), left and right swing (PITCH), and horizontal rotation (YAW), as shown in the following figure.
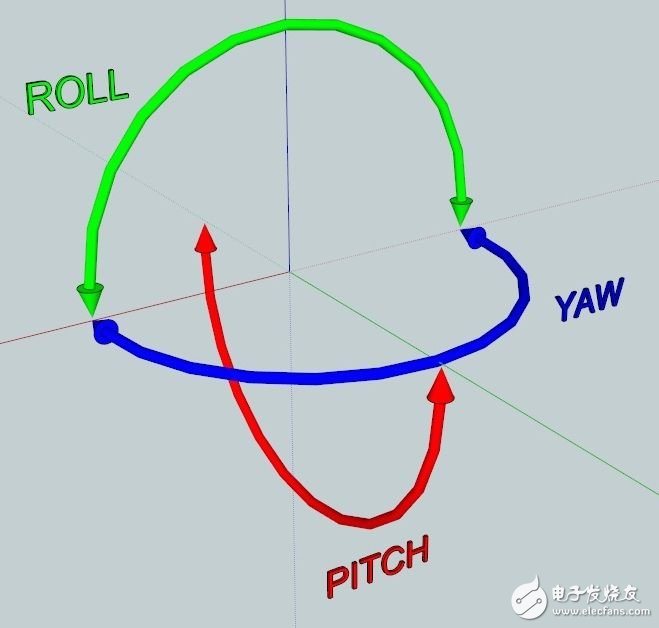
These two categories, each class of three degrees of freedom, add up to 6 degrees of freedom.
There are two different directions in each degree of freedom. For example, the movement of the elevator has only one degree of freedom: up and down, but in this degree of freedom it can choose to go up or down; for the same reason, the tire rotates only one degree of freedom, but it can choose to rotate clockwise or counterclockwise.
The movement of any hard object, no matter how complex, can be explained by displacement and rotation (soft objects, such as expansion and contraction, such as balloons). For example, a bumper car has only three degrees of freedom: it can rotate in the horizontal plane or shift back and forth, left and right, but can't move up and down, flip back and forth or swing left and right (if no accidents occur).
It is much easier to explain the Daydream handle at this time. First of all, it is a snap, but it can only track the degrees of freedom of front and back flip, left and right swing and horizontal rotation. It is impossible to know the displacement of the handle in space. Therefore, if you want to accurately describe the Daydream handle, you should call it a 3 degree of freedom or 3DOF snap handle.
In contrast, HTC Vive's tracking system gives the handle 6 degrees of freedom, including 3 degrees of freedom of displacement. The result is that you can't use Daydream's handles to do the same thing as picking up items on the ground, but the Vive's handles can.
The following two videos show what the Daydream controller can do, and what Vive can do but what Daydream can't do, all from Google.
Daydream handle demo, 3 degrees of freedom:
Http://v.qq.com/boke/page/z/0/6/z03027aria6.html
Daydream Lab - Drum Keys, 6 degrees of freedom:
Http://v.qq.com/boke/page/o/0/8/o0302pcjyc8.html
IMU and inertia
IMU is the abbreviation of InerTIal Measurement Unit, which is the inertial measurement unit. It usually consists of three sensors: accelerometer, gyroscope and magnetometer. It used to be mainly used on airplanes. Now most smartphones are available, and the cost is relatively low. Using the IMU, you can measure speed, direction, and gravity. This kind of motion capture technology is what we often call inertia.
The IMU can track the movement of the object with three degrees of rotational freedom. The Daydream handle can definitely use the IMU sensor. And that's why Google can let developers use an Android phone instead of the Daydream handle for development, because there is also an IMU on the phone.
The problem of inertial motion capture is that it is difficult to judge the absolute position of an object in space, and thus the three degrees of freedom of displacement motion cannot be tracked.
Optical capture
In addition to inertial motion capture, another commonly mentioned technique is optical motion capture, or optical spatial positioning, which allows the displacement and rotation of an object to be determined by precise spatial position. There are many kinds of optical motion capture. Here, the technique with Mark points is taken as an example.
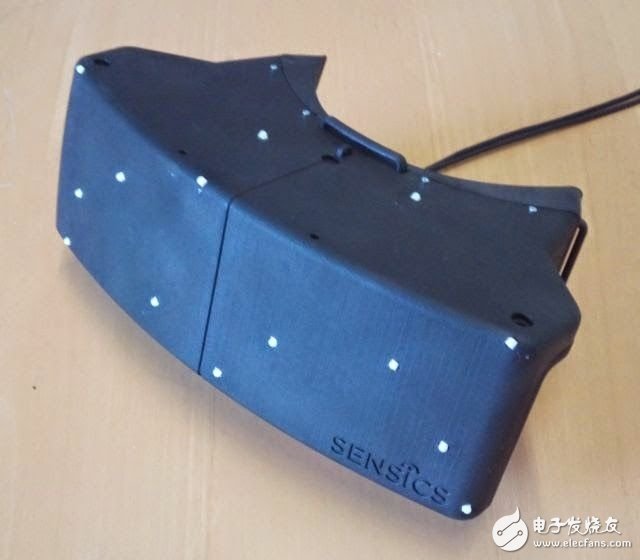

Sensics dSight headed infrared Mark points
Optical motion capture continuously tracks the Mark points on an object through one or more cameras. The points are arranged in a specific pattern and then a series of algorithms are used to determine the position of the object. The algorithm determines the absolute position and rotation direction of the object by comparing the position of the known Mark point with the position of the Mark point on the object.
The number, location and arrangement of Mark points are scientifically based. For example, if you only use 4 Mark points that form a square, you can't tell if the object is upside down or rotated 90 degrees. In addition, if the Mark point is blocked or cannot be tracked by ambient light, it will affect the position determination.
At this point, more cameras and computing performance are usually required for continuous and accurate tracking, resulting in a significant increase in cost. Therefore, many providers of motion capture technologies, such as Novo, will use optical and inertial motion capture to achieve accurate tracking of 6 degrees of freedom, thereby reducing the number of cameras used and the need for computational performance, and controlling costs.
to sum up
Various tracking techniques for VR are used to achieve high-precision, low-cost 6-DOF motion tracking. At present, the three degrees of freedom of the object rotation by the IMU are mature, so it is applied to various schemes; and the technique of judging the displacement by spatial positioning also has the lower cost scheme of Vive Lighthouse. However, the cost of many optical capture programs is still high. There are many other types of techniques besides the above schemes, and there are many other tracking techniques in addition to optical motion capture.
Map and reference source: RoadtoVR
Guangzhou Yunge Tianhong Electronic Technology Co., Ltd , http://www.e-cigaretteyfactory.com