[Home Theater Network HDAV.com.cn] The success of a home theater is the most intuitive performance. However, the sound is not good, in addition to the factors of the audio equipment used, there are also the influence of equipment matching, adjustment and space factors. Among them, the spatial factor is the most influential and the most difficult to overcome. The acoustic properties of the various types of rooms will have a variety of effects on the playback of the sound, and the size and proportion of the room is a vital part.

Below, Xiaobian will work with you to understand the principle of proportional design of audio-visual space rooms, and to understand the proportion of internationally recognized audio-visual space rooms.
First, the principle of the proportional design of the audiovisual space room
1. Bolt-Area
In the research and discussion of the proportion of rooms in the early part of the last century, the most successful results came from the Bolt-Area brought by the famous acoustic expert Bolt, which transformed the blunt digital ratio into specific images. range. Bolt assumes that the natural resonant frequency of a rigid rectangular room is evenly separated, so it will be flatter on the sound frequency response curve without excessive peaks and valleys. However, as far as the current acoustic theory is concerned, it is not ideal to use the average mode interval as the basic theory, but at the time, it cannot be said that it is a major breakthrough.
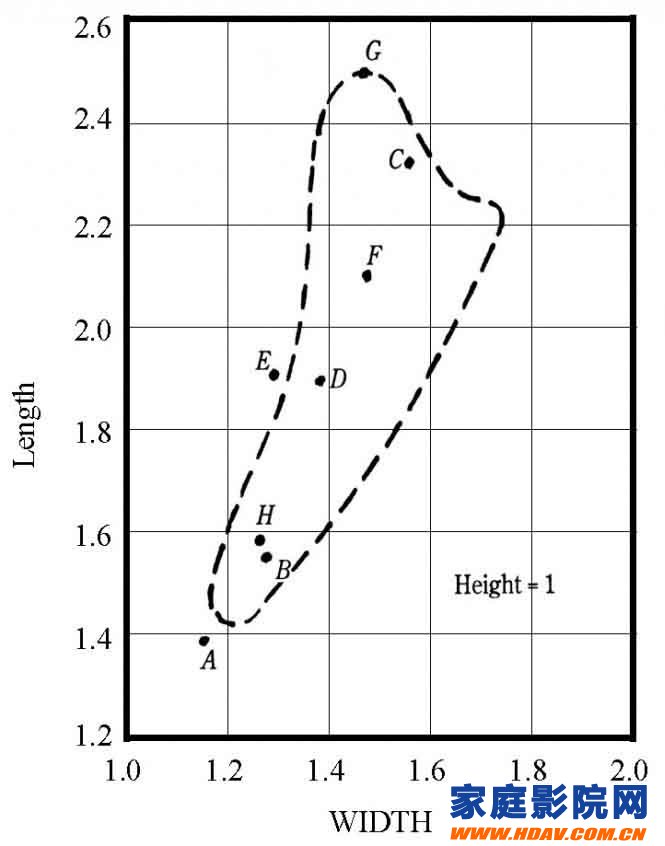
Bol line
The study of the proportion of the room in the later generations by the Boer line has been greatly helpful. The horizontal axis in the figure is W (room width ratio), the vertical axis is L (room length ratio), and the height ratio of the room is set to 1. Bolt believes that the range inside the closed curve is the ideal ratio of the room, and this closed curve is derived for small and medium-sized rooms. The left side of the curve corresponds to a relatively small room, and the right side corresponds to the corresponding volume. Larger room. In the same year, Bolt also noticed that there are also a number of acceptable room proportions in areas outside the closed curve, which is determined by the fact that the theory based on the average mode interval is still flawed.

2, small room acoustic system
Talking about the acoustic defects of the home audio-visual space, it is inevitable to connect to the small room acoustic system. Due to the small volume of the room, the length of the three sides and the wavelength of the acoustic wave can produce a certain proportional relationship, which will inevitably cause the sound superimposition or attenuation of a certain frequency band due to the natural resonant frequency mode of the room, resulting in the problem of room sounding, resulting in The sound quality of the room dropped.

Acoustic defects in home audiovisual spaces include acoustic defects such as standing waves, comb filtering, resonance and degeneracy. Among them, the standing wave, resonance and degeneracy are related to the size and proportion of the room. When the size of the room is close to the wavelength of the low frequency part or is in a simple multiple relationship with the wavelength of the low frequency part, the standing wave phenomenon occurs in the room. There are three ways of room resonance, including axial resonance, tangential resonance and oblique resonance.
The figure below shows the room resonance map:
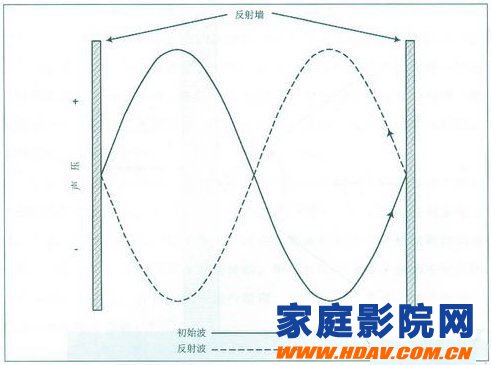
When the sound frequency of the user's sound system is the same as a certain natural frequency in the room, the whole room will resonate at that frequency, causing the sounds at certain fixed positions in the room to superimpose and become peak. The sound becomes louder; at the same time, the sound in a certain fixed position in the room has a valley value, and the sound becomes weak, which forms a standing wave.

Second, the development of the size and proportion of the room of audio-visual space
Since the last century, the exploration of the proportion of rooms in the audiovisual space has emerged in an endless stream. Below we will start from the early audio-visual space room recommendation ratio, the current well-known audio-visual space room proportion range calculation method and the current domestic and international organizations and institutions on the recommended size of the room size and proportion of the audio-visual room, the size and proportion of the audio-visual space room Study the development process to make a review.
1. Recommended proportion of early famous audio-visual space rooms
The research on the size and proportion of the room in the audio-visual space has been paid attention to by many famous acoustic experts since the 1940s. It is found that the proportion and size of the room are two mutually influential room acoustic characteristics. At first, most of the research was carried out in the environment of auditorium, recording studio, etc. After decades of development, with the maturity and popularity of home theaters, the size and proportion of rooms in small-space home audio-visual spaces have also appeared internationally. standard. Today, the vast majority of outstanding home theater audiovisual spaces are built on top of these standards.
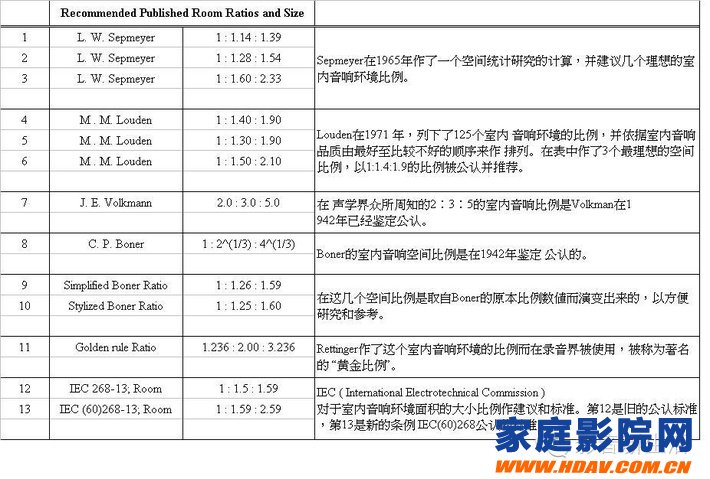
Regarding the shape of the room in the audio-visual space, these acoustic experts believe that rectangular rooms are easy to construct and acoustically controlled, while any environment should avoid concave surfaces as much as possible, because it causes acoustic focus and blind spots, and it is difficult to eliminate the effects. The following are the recommended ratios of the most famous acoustic experts (height: width: long):
A, Sabine 1:1.5:2.5
Acoustic simulation of this ratio:
Height: 3m, width: 4.5m, length: 7.5m, area: 33.75m2, volume: 101.25m3
B, Volkmann 1:1.6:2.5
Acoustic simulation of this ratio:
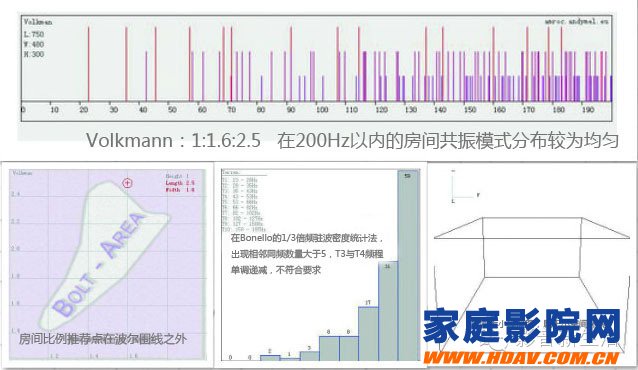
Height: 3m, width: 4.8m, length: 7.5m, area: 23.04m2, volume: 69.12m3
C, Knudsen 1:1.88: 2.5
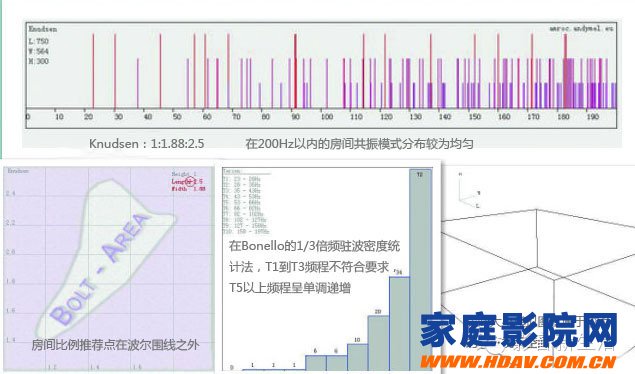
Height: 3m, width: 5.64m, length: 7.5m, area: 42.3m2, volume: 126.9m3
D, Harmonic 1:2:3
Acoustic simulation of this ratio:
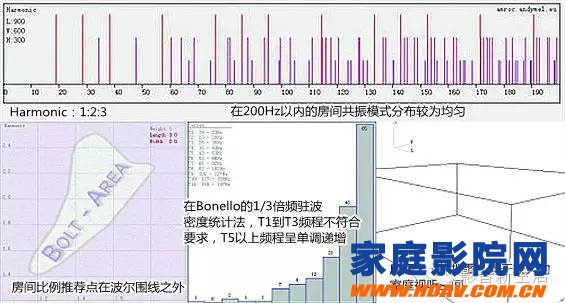
Height: 3m, width: 6m, length: 9m, area: 54m2, volume: 162m3
E, Boner 1:1.26: 1.59
Acoustic simulation of this ratio:
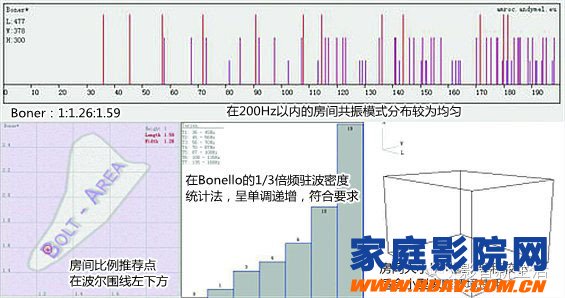
Height: 3m, width: 3.78m, length: 4.77m, area: 18m2, volume: 54m3
F, golden ratio 1:1.62: 2.62
Acoustic simulation of this ratio:
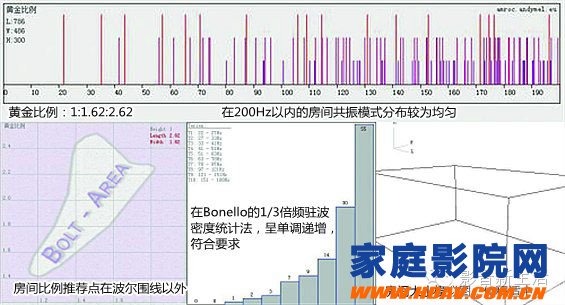
In addition, there are 1:1.67:2.67 recommended by early European acoustic experts. It can be known from the ratio of the seven recommended rooms that the scope of the room ratio is roughly set within the range of 1: (1~2): (1.5~3), although the recommended ratio of the above several rooms is larger for the volume. The concert hall was set up, but it also laid a solid foundation for the establishment of the standard of the small room in the later period. Of noteworthy is the 1:1.26:1.59 recommended by Boner, which is the proportion of rooms recommended for smaller broadcast studios, and eventually became the predecessor of international standards for home theater audiovisual space.

2, the calculation method of the proportion range of the audio-visual space room
Based on the research results of early acoustic experts on the proportion of rooms, since the 1960s to the present, new methods for calculating the optimal range of room ratios have emerged, among which the following are more famous:
A, Gilford: loose resonance frequency statistics
Gilford performs a lookup grouping of the standing wave bandwidth of approximately 20 Hz, changing the size of the room, and continuously calculating until a satisfactory average distribution occurs. At that time, Gilford was done by hand calculations, and the amount of work was great. Gilford also pointed out at the time that Bolt's proposed 1:1.5:2.5 ratio had some problems because the axial mode caused changes in the acoustic properties of the room.

B, Louden: Statistical method for standard deviation uniformity of resonance frequency distribution
In 1971, the famous acoustic expert Louden used the uniformity statistical method of the standard deviation of the resonance frequency distribution, and the calculation accuracy was more accurate than the average difference statistical method proposed by the early Bolt. Louden calculates the first 36 resonant frequencies and their standard deviations in 125 rectangular rooms with a proportional interval of 0.1 in the range of 1:(1.1 to 1.9): (1.1 to 2.8). In order to avoid the influence of the volume of the room, the volume of each proportion selected by Louden was 201.6 cubic meters, and then the standard deviation was used to judge the proportion of the size ratio of the 125 rooms.
This resulted in a ratio of 1:1.4:1.9 recommended by the International Broadcasting and Television Organization and the European Broadcasting Union, and the ratio of classic rooms such as 1:1.5:2.1, 1:1.4:2.1 and 1:1.6:2.1 appeared in Louden. Among the research results. The ratio of the room ratio obtained from the study of Louden is compared with the Boer line drawn by Bolt. The best three values ​​are in the middle of the line, which is quite close to the Bol line, and the best choice for future generations. The room size ratio is convenient.

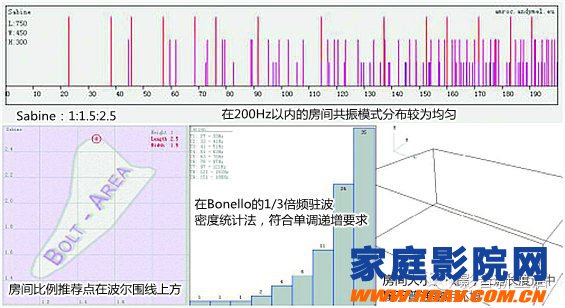
C, Bonello: 1/3 octave standing wave density statistical method
In 1981, another acoustic expert, Bonello, conducted a new study on the statistical method of room ratio. The main reason for Bonello's research is that the standing wave density is not reduced when 1/3 octave to higher bandwidth, and 5 or more consistent frequency modes are acceptable in 1/3 octave. of. Bonello believes that a good audio-visual spatial resonance frequency is monotonically increasing in the 1/3 octave frequency, and the number of resonant frequencies in the latter frequency is always more than the adjacent previous frequency.
A new kind of statistical method has appeared: just calculate the resonance frequency of the low frequency band of various proportions of the room, and analyze the number of resonance frequencies in each 1/3 frequency range. If it is monotonically increasing, then the room size ratio is Preferably.

Bonello also compared his findings with Bolt's Boer line and found that some ratios in the closed curve were not sufficient, and some proportions outside the curve were acceptable. In addition, Bonello pointed out that the distribution of the resonant frequency is related to the volume of the room in addition to the ratio of the length to the height of the room.
For a suitable proportion of a small volume room, it may not be suitable in a room with a large volume. The opposite is also true. Among them, Bonello found a ratio of 1:1.25:1.6, and for 60m2, 200m2 and 400m2, it also meets the requirement of monotonically increasing resonance density distribution density. Bonello's theory has achieved great results in the design of professional studios and studios.

3. Recommended standards for the size and proportion of rooms in the audio-visual room
After the research and accumulation of predecessors, at present, regarding the shape, size and proportion of audio-visual space, domestic and foreign organizations and institutions have established relevant standards and recommendations, including the International Electrotechnical Commission, International Broadcasting and Television Organization, European Broadcasting Union, Dolby , THX, PMI, Tsinghua University, etc.
Among these regulations, especially the IEC29-B family audio-visual space standard brought by the International Electrotechnical Commission, it is the key standard for home theater room design reference. And Dolby's recommendations for the top film review studios are also important for the design of home theater audiovisual spaces. Because the predecessor of the home theater is the film late review room, the film late review room is the standard for home theater construction. Relatively speaking, the room size and scale standards recommended by the International Broadcasting Organization and the European Broadcasting Union are tailored to the broadcast studio environment, and there are still some differences from the home environment.

It is worth noting that when you refer to the relevant standards, in addition to paying attention to the recommended ratio of the room, you also need to pay attention to the recommended room volume, both of which will affect the acoustic characteristics of the room. The recommended ratio of the larger volume of the room may not be suitable as the recommended ratio for rooms with smaller volumes.
In addition, in various recommendation standards, the discussion of the shape of the room has also been carried out. For example, THX and PMI believe that in addition to the rectangular room shape, other shapes of the room can also be used as the audiovisual space (excluding Square), but it is not recommended because it is difficult to predict, calculate and control the acoustic properties of the room.

A, IEC29-B home listening room design standards
Regarding the establishment criteria of the audio-visual room, the IEC29-B home audio-visual room standard established by the IEC is the most authoritative standard. Compared with the IEC268-13 audio-visual room standard brought by the IEC earlier, the IEC29-B standard is more detailed and accurate, and is suitable for use in a small room, which is convenient for users to establish a home theater audio-visual room under the ordinary home environment. Since the IEC organization is based in Europe, the IEC29-B standard also provides recommendations on the length, proportion, room area and reverberation time of the three sides of the room based on the state of the European home environment.

In terms of the shape of the room, it is recommended that the best room shape is rectangular, and the slightly trapezoidal quadrilateral is also accepted, but it is never recommended to use a square or a narrow shape to reduce the serious problem of room sounding caused by low frequency resonance. The recommended room ratio is 1:1.6:2.4 (height: width: long), and the recommended room size should be above 24m2. In addition, the IEC29-B standard also specifies the interior decoration of the room, requiring the floor in front of the speaker to have no sound-absorbing materials such as carpet. The back of the speaker and the ceiling of the ceiling are reflective, and the front of the speaker is sound-absorbing.
B, Dolby recommended in the design of the room for the final film review room
Dolby has a unique aspect in the design of the film's post-review room, specifically in the certification of Dolby's top PREMIER STUDIO film review studio, which mentions room design. Claim. Dolby believes that the best room size should be above 45m2, and the best room volume should be above 150m3. As a result, it can be found that the room having too small a space is inferior in characteristics, and at the same time, it is more difficult to perform acoustic processing.

C. Recommendations for the proportion and volume of rooms in the international standard EBU (European Broadcasting Union) of professional broadcasters
The room design of the professional broadcast audition room actually belongs to the room acoustics of the small space, and it is actually the same as the home audio-visual room. EBU and OIRT have common recommendations for the proportion and size of broadcast room rooms, with 1:1.4:1.9 and 120m3 as the best ratio of stereo audition room and room volume. This ratio is widely used in broadcasting audit rooms in European countries. designing. It is worth noting that this reference standard is based on the reference standard obtained by the Louden resonance frequency distribution standard deviation uniformity statistics method at the same time, and also fully meets the proportion of rooms recommended by the Boer line. Recommended room ratio (height: width: long): 1:1.4:1.9, recommended room volume: 120m3.
D. Domestic related home audio-visual room standards
Looking around the global IEC29-B standard has become the mainstream of home audio-visual room design standards. However, there are also standards for the design of home audio-visual room rooms. The National Standard for Speaker Listening Tests specifies the optimal reverberation time for audio-visual rooms. The General Specification for Surround Sound Amplifiers for Home Theaters regulates home theater audiovisuals. The basic characteristics of the room, the room scale and volume recommended standards are in the "General Specifications for Surround Sound Amplifiers for Home Theater." The "General Specification for Surround Sound Amplifiers for Home Theaters" believes that the audio and video response curves in the audio-visual room should be as smooth as possible without significant acoustic staining.

In the frequency range of 100 ~ 5000 Hz, there should be no abnormal resonance and tremor echo in the room. As for the noise floor in the empty field (no listener), the noise floor level measured in the listening area of ​​the listening room should be less than 35 dB (A weighted, slow). The recommended volume of the audio-visual room is 80 m3, the height is 2.8 m, the length is 6.7 m, the width is 4.2 m, and the ratio of the room is 1:1.5:2.39. Place this recommended room ratio in the Bol encircle, just within the closed curve, which is one of Bolt's recommended room proportions. From China's recommendation on the proportion and volume of the room, it is not difficult to find that this is very consistent with the international standards, indicating that China has been fully integrated with the international community in the acoustic design of the room. Recommended room ratio (height: width: long): 1:1.5:2.39, recommended room volume: 80m3.

E. Suggestions on Tsinghua University's design of home audio-visual room
Tsinghua University also has considerable research in architectural acoustics, including the design of home audio-visual rooms in small spaces. Tsinghua University believes that the regular room shape is likely to cause acoustic defects indoors, especially when the ratio of length to width of space is an integer ratio. Therefore, it is possible to adjust the length, width and height ratio of the room while determining the size of the room at the beginning of the design of the viewing room. The ratio of the length, width and height of an ideal room should be 1:1.4:1.26, but such a ratio is difficult to achieve in architectural design conditions. The recommended ratios in the table below can be used as a reference:

Taking the recommended ratio in the above table, the indoor resonance mode can be evenly distributed within the range of the full frequency band, avoiding concentration in the vicinity of a certain frequency band, resulting in room sounding. Tsinghua University does not place any emphasis on the volume of the room. In fact, since these ratios are small spaces built in the home audio-visual room, they are all used in the ordinary family environment. In the process of selecting, you can combine the shape of the room. To consider it comprehensively, you don't have to stick to a certain optimal ratio.
Conclusion : The proportion and size of the room is an important basis for constructing an ideal audiovisual space. By understanding the proportion of rooms in the internationally recognized audiovisual space, we can help us better perform indoor acoustic design to get the desired listening effect. More fresh and fun home theater information, please pay attention to home theater network http:// (WeChat: cnhifi), the country's most influential home theater audio player interactive media website.
Note: This article is transferred from the new life of audio and video. The article is an independent view of the author and does not represent the position of the home theater network.
Multicore Silicone Cable,Insulated Wire,Insulated Silicone Cable,Oil Proof Silicone Wire
JIANGSU PENGSHEN HIGH TEMPERATURE WIRE CABLE CO., LTD. , https://www.pengshencable.com